Vertex AI Search Grounding for agents¶
Vertex AI Search 是 Agent Development Kit (ADK) 的强大工具,使 AI 智能体能够访问你的私有企业文档和数据仓库中的信息。通过将智能体连接到已索引的企业内容,你可以为用户提供基于组织知识库的答案。
此功能对于需要内部文档、政策、研究论文或任何已在 Vertex AI Search 数据存储中索引的专有内容的企业级查询尤为有价值。当你的智能体判断需要知识库中的信息时,它会自动搜索已索引文档,并将结果与正确的出处整合到回复中。
你将学到什么¶
在本指南中,你将了解:
- 快速上手:如何从零创建并运行支持 Vertex AI Search 的智能体
- Grounding 架构:企业文档 grounding 的数据流与技术流程
- 响应结构:如何解读 grounding 响应及其元数据
- 最佳实践:向用户展示引用和文档出处的建议
Vertex AI Search Grounding 快速上手¶
本快速入门指南将引导你创建一个具有 Vertex AI Search grounding 功能的 ADK 智能体。本快速入门假设你使用本地 IDE(VS Code 或 PyCharm 等),安装了 Python 3.10+,并可以访问终端。
1. 准备 Vertex AI Search¶
如果你已有 Vertex AI Search 数据存储及其数据存储 ID,可跳过本节。否则,请按照 Get started with custom search 的指引,完成 Create a data store(选择 Unstructured data 标签)。你将以 Alphabet investor site 的财报 PDF 构建一个示例数据存储。
完成数据存储创建后,打开 Data Stores,选择你创建的数据存储,找到 数据存储 ID:
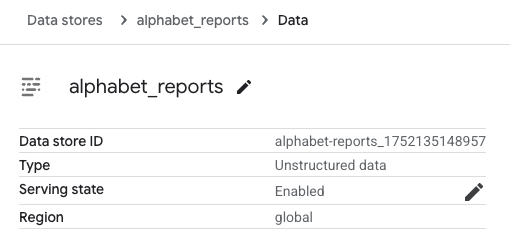
记下此 数据存储 ID,后续会用到。
2. 设置环境并安装 ADK¶
以下是为 Python 和 TypeScript 项目设置环境和安装 ADK 的步骤。
3. 创建智能体项目¶
在项目目录下,运行以下命令:
编辑 agent.py¶
将以下代码复制到 agent.py,并将 配置 部分的 YOUR_PROJECT_ID 和 YOUR_DATASTORE_ID 替换为你的项目 ID 和数据存储 ID:
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.tools import VertexAiSearchTool
# 配置
DATASTORE_ID = "projects/YOUR_PROJECT_ID/locations/global/collections/default_collection/dataStores/YOUR_DATASTORE_ID"
root_agent = Agent(
name="vertex_search_agent",
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
instruction="使用 Vertex AI Search 回答问题,从内部文档中查找信息。在可用时始终引用来源。",
description="具有 Vertex AI Search 功能的企业文档搜索助手",
tools=[VertexAiSearchTool(data_store_id=DATASTORE_ID)]
)
此时你的目录结构应如下:
4. 身份验证设置¶
注意:Vertex AI Search 需要 Google Cloud Platform(Vertex AI)认证。不支持 Google AI Studio。
- 设置 gcloud CLI
- 通过终端运行
gcloud auth login认证 Google Cloud。 -
打开
.env文件,复制如下内容并更新项目 ID 和地区:
5. 运行你的智能体¶
运行以下命令启动开发 UI。
Note for Windows users
如果遇到 _make_subprocess_transport NotImplementedError,请尝试使用 adk web --no-reload。
第 1 步: 打开提供的 URL(通常是 http://localhost:8000 或 http://127.0.0.1:8000)到浏览器。
第 2 步: 在 UI 左上角下拉菜单中选择你的智能体 "vertex_search_agent"。
故障排查
如果下拉菜单中没有 "vertex_search_agent",请确保你在智能体文件夹的父目录(即 vertex_search_agent 的父目录)下运行 adk web。
第 3 步: 现在你可以通过文本框与智能体对话。
📝 可用于尝试的提示词示例¶
通过这些问题,你可以确认智能体确实调用了 Vertex AI Search 获取 Alphabet 报告信息:
- 2022 年 Q1 Google Cloud 的收入是多少?
- YouTube 呢?

你已成功用 ADK 创建并与 Vertex AI Search 智能体交互!
Vertex AI Search grounding 的工作原理¶
Vertex AI Search grounding 让你的智能体连接到组织已索引的文档和数据,使其能基于企业私有内容生成准确回复。当用户的问题需要内部知识库信息时,智能体底层的 LLM 会智能决定调用 VertexAiSearchTool,从已索引文档中查找相关事实。
数据流示意图¶
下图展示了用户提问到 grounding 响应的逐步流程。
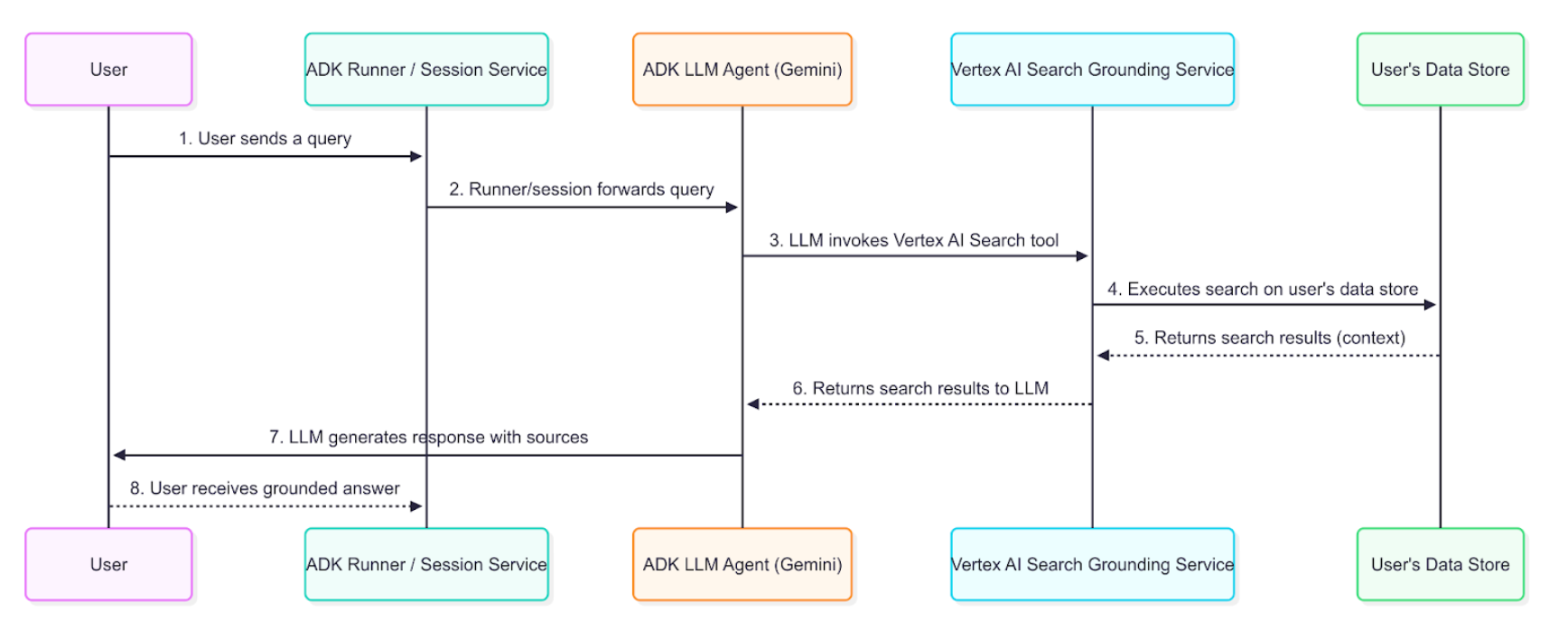
详细说明¶
grounding 智能体使用上述数据流,从企业信息检索、处理并整合到最终用户回复中。
- 用户提问:终端用户向智能体提问,内容涉及内部文档或企业数据。
- ADK 编排:ADK 负责编排智能体行为,将用户消息传递给智能体核心。
- LLM 分析与工具调用:智能体的 LLM(如 Gemini 模型)分析提示,如判断需要知识库信息,则触发 grounding 机制,调用 VertexAiSearchTool。这适用于公司政策、技术文档或专有研究等问题。
- Vertex AI Search 服务交互:VertexAiSearchTool 与配置好的 Vertex AI Search 数据存储交互,后者包含已索引的企业文档。服务会针对私有内容构建并执行搜索查询。
- 文档检索与排序:Vertex AI Search 根据语义相似度和相关性评分,从数据存储中检索并排序最相关的文档片段。
- 上下文注入:搜索服务在生成最终回复前,将检索到的文档片段注入模型上下文。这一步让模型能“推理”企业事实数据。
- 生成有据可依的回复:LLM 结合相关企业内容,生成包含文档信息的回复。
- 带出处的回复展示:ADK 收到最终 grounding 回复,其中包含必要的文档引用和 groundingMetadata,并将其带出处地展示给用户。终端用户可据此验证企业信息。
理解 Vertex AI Search grounding 响应¶
当智能体用 Vertex AI Search grounding 回复时,会返回详细信息,包括最终文本答案和用于生成答案的文档元数据。这些元数据对于验证回复和提供企业出处至关重要。
有据可依的回复示例¶
以下是模型针对企业文档 grounding 查询后返回的内容对象示例。
最终答案文本:
"开发医疗抄写员模型面临诸多重大挑战,主要由于医疗文档的复杂性、涉及的敏感数据以及临床工作流的高要求。关键挑战包括:**准确性与可靠性:** 医疗文档要求极高的准确性,错误可能导致误诊、错误治疗和法律后果。确保 AI 模型能可靠捕捉细致的医学语言、区分主观与客观信息,并准确转录医患对话,是一大难题。**自然语言理解(NLU)与语音识别:** 医疗对话通常语速快,涉及高度专业术语、缩写,且说话者口音多样……[回复继续,详细分析隐私、集成和技术挑战]"
Grounding 元数据片段:
这是你会收到的 grounding 元数据。在 adk web 的 Response 标签页可查看:
{
"groundingMetadata": {
"groundingChunks": [
{
"document": {
"title": "AI in Medical Scribing: Technical Challenges",
"uri": "projects/your-project/locations/global/dataStores/your-datastore-id/documents/doc-medical-scribe-ai-tech-challenges",
"id": "doc-medical-scribe-ai-tech-challenges"
}
},
{
"document": {
"title": "Regulatory and Ethical Hurdles for AI in Healthcare",
"uri": "projects/your-project/locations/global/dataStores/your-datastore-id/documents/doc-ai-healthcare-ethics",
"id": "doc-ai-healthcare-ethics"
}
}
// ... 其他文档
],
"groundingSupports": [
{
"groundingChunkIndices": [0, 1],
"segment": {
"endIndex": 637,
"startIndex": 433,
"text": "确保 AI 模型能可靠捕捉细致的医学语言……"
}
}
// ... 更多支持信息,关联文本片段与来源文档
],
"retrievalQueries": [
"challenges in natural language processing medical domain",
"AI medical scribe challenges",
"difficulties in developing AI for medical scribes"
// ... 其他搜索查询
]
}
}
如何解读响应¶
元数据将模型生成的文本与企业文档建立了关联。分解如下:
- groundingChunks:模型参考的企业文档列表。每个 chunk 包含文档标题、uri(文档路径)和 id。
- groundingSupports:该列表将最终答案中的特定句子与
groundingChunks关联。 - segment:标识最终答案文本的具体片段,由
startIndex、endIndex和text定义。 - groundingChunkIndices:数组,包含与
groundingChunks源对应的索引号。例如,关于“HIPAA 合规性”的文本由索引为 1 的文档("Regulatory and Ethical Hurdles")支持。 - retrievalQueries:展示为查找相关信息而对数据存储执行的具体搜索查询。
如何展示 Vertex AI Search grounding 响应¶
与 Google Search grounding 不同,Vertex AI Search grounding 不要求特定的展示组件。但展示引用和文档出处有助于建立信任,让用户可验证企业权威信息。
可选的引用展示¶
由于提供了 grounding 元数据,你可以根据应用需求实现引用展示:
简单文本展示(最小实现):
for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
print(event.content.parts[0].text)
# Optional: Show source count
if event.grounding_metadata:
print(f"\n基于 {len(event.grounding_metadata.grounding_chunks)} 个文档")
增强型引用展示(可选): 你可以实现交互式引用,展示每句话由哪些文档支持。grounding 元数据提供了将文本片段映射到来源文档的全部信息。
实现注意事项¶
实现 Vertex AI Search grounding 展示时:
- 文档访问:验证用户对引用文档的访问权限
- 简单集成:基础文本输出无需额外展示逻辑
- 可选增强:仅在需要出处时添加引用
- 文档链接:如有需要,将文档 URI 转为内部可访问链接
- 搜索查询:retrievalQueries 数组展示了对数据存储执行的搜索内容
总结¶
Vertex AI Search Grounding 让 AI 智能体从通用助手转变为企业级知识系统,能够基于组织私有文档提供有出处、可验证的信息。集成此功能后,你的 ADK 智能体将能够:
- 访问已索引文档仓库中的专有信息
- 提供来源出处,增强透明度与信任
- 输出包含可验证企业事实的完整答案
- 在 Google Cloud 环境内保持数据隐私
grounding 过程无缝连接用户提问与组织知识库,在保持对话流畅的同时,为回复注入相关企业上下文。合理实现后,你的智能体将成为企业信息发现与决策的强大工具。