自定义音频流式传输应用(WebSocket)¶
本文概述了使用 ADK 双向流式传输和 FastAPI 构建的自定义 Bidi 流式传输 web 应用的服务器和客户端代码,通过 WebSockets 启用实时、双向音频和文本通信。
注意: 本指南假设你有 JavaScript 和 Python asyncio 编程经验。
支持语音/视频流的模型¶
要在 ADK 中使用语音/视频流,你需要使用支持 Live API 的 Gemini 模型。你可以在文档中找到支持 Gemini Live API 的 模型 ID:
1. 安装 ADK¶
下载示例代码:
curl -L https://github.com/google/adk-docs/archive/refs/heads/main.tar.gz | \
tar xz --strip=5 adk-docs-main/examples/python/snippets/streaming/adk-streaming-ws
cd adk-streaming-ws
创建并激活虚拟环境(推荐):
# 创建
python -m venv .venv
# 激活(每个新终端)
# macOS/Linux: source .venv/bin/activate
# Windows CMD: .venv\Scripts\activate.bat
# Windows PowerShell: .venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
安装 ADK:
使用以下命令设置 SSL_CERT_FILE 变量。
导航到应用文件夹:
此示例代码包含以下文件和文件夹:
adk-streaming-ws/
└── app/ # web 应用文件夹
├── .env # Gemini API 密钥 / Google Cloud 项目 ID
├── main.py # FastAPI web 应用
├── static/ # 静态内容文件夹
| ├── js # JavaScript 文件文件夹(包含 app.js)
| └── index.html # web 客户端页面
└── google_search_agent/ # 智能体文件夹
├── __init__.py # Python 包
└── agent.py # 智能体定义
2. 设置平台¶
要运行示例应用,请从 Google AI Studio 或 Google Cloud Vertex AI 中选择一个平台:
- 从 Google AI Studio 获取 API 密钥。
-
打开位于 (
app/) 内的.env文件,并复制粘贴以下代码。 -
将
PASTE_YOUR_ACTUAL_API_KEY_HERE替换为你的实际API KEY。
- 你需要一个现有的
Google Cloud 账户和一个项目。
*设置一个
Google Cloud 项目
- 设置
gcloud CLI
*通过在终端运行
gcloud auth login向 Google Cloud 进行身份验证。 - 启用 Vertex AI API。
- 设置
gcloud CLI
*通过在终端运行
-
打开位于 (
app/) 内的.env文件。复制粘贴 以下代码并更新项目 ID 和位置。
agent.py¶
google_search_agent 文件夹中的智能体定义代码 agent.py 是编写智能体逻辑的地方:
import os
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.tools import google_search # 导入工具
root_agent = Agent(
name="google_search_agent",
model=os.getenv("DEMO_AGENT_MODEL"),
description="使用 Google 搜索来回答问题的智能体。",
instruction="使用 Google 搜索工具来回答问题。",
tools=[google_search],
)
注意: 此应用程序使用 Gemini Live API(也称为 bidiGenerateContent),该 API 为文本和音频/视频输入启用实时双向流式传输。模型必须支持 Live API 才能使双向流式传输正常工作。通过以下方式验证模型功能:
智能体使用 DEMO_AGENT_MODEL 环境变量(来自 .env 文件)中指定的模型。
注意你如何轻松集成 Google 搜索基础 功能。Agent 类和 google_search 工具处理与 LLM 的复杂交互以及与搜索 API 的基础,让你专注于智能体的 目的 和 行为。
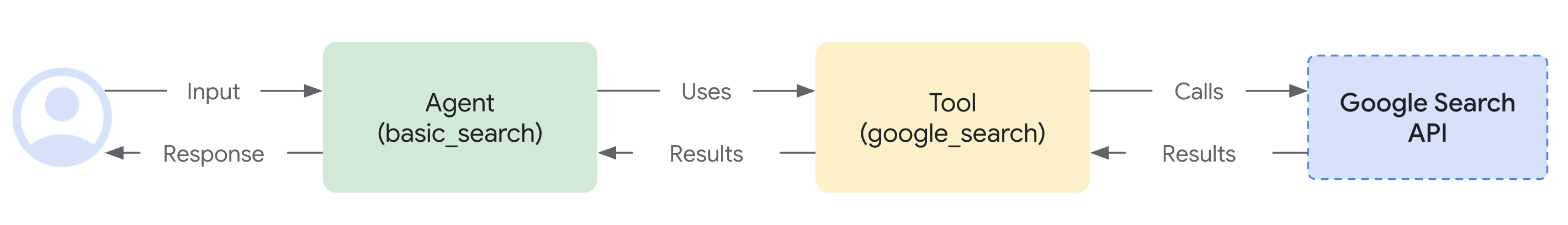
3. 与你的流应用交互¶
- 导航到正确的目录:
要有效运行你的智能体,请确保你在 app 文件夹 (adk-streaming-ws/app) 中
- 启动 Fast API: Run the following command to start CLI interface with
- 使用文本模式访问应用: 应用启动后,终端将显示一个本地 URL(例如,http://localhost:8000)。点击此链接在浏览器中打开 UI。
现在你应该看到如下所示的 UI:
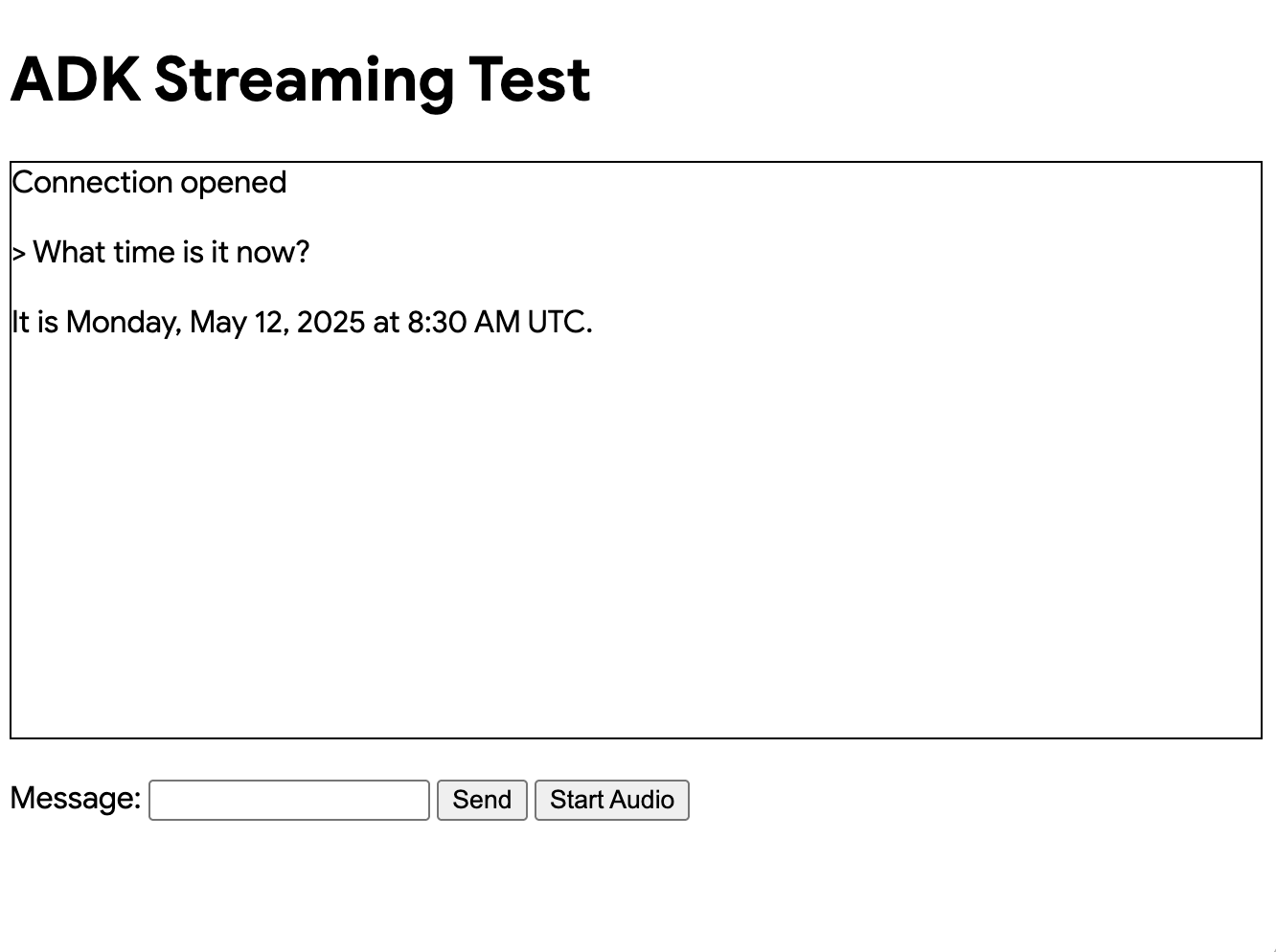
尝试提问 What time is it now?。智能体将使用 Google 搜索回应你的查询。你会注意到 UI 以流式文本显示智能体的回应。你也可以随时向智能体发送消息,即使智能体仍在回应中。这展示了 ADK Streaming 的双向通信能力。
- 使用音频模式访问应用: 现在点击
Start Audio按钮。应用以音频模式与服务器重新连接,并且 UI 将在第一次显示以下对话框:
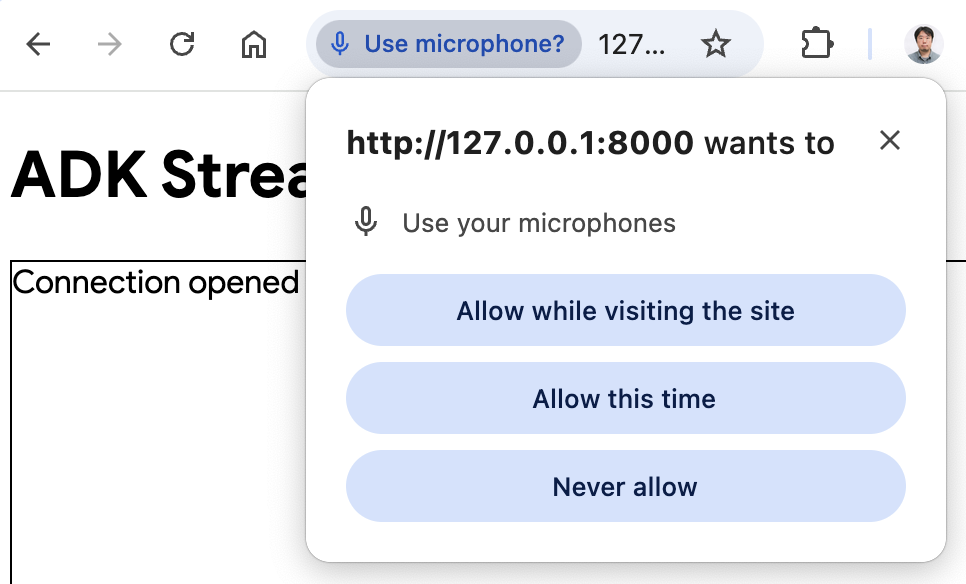
点击 Allow while visiting the site,然后你将看到麦克风图标显示在浏览器顶部:
现在你可以用语音与智能体交谈。用语音提问类似 What time is it now? 的问题,你也会听到智能体用语音回应。由于 ADK 的 Streaming 支持 多种语言,它也可以用支持的语言回应问题。
- 检查控制台日志
如果你使用 Chrome 浏览器,右键点击并选择 Inspect 打开 DevTools。在 Console 中,你可以看到传入和传出的音频数据,例如 [CLIENT TO AGENT] 和 [AGENT TO CLIENT],表示浏览器和服务器之间流入和流出的音频数据。
同时,在应用服务器控制台中,你应该会看到类似这样的内容:
INFO: ('127.0.0.1', 50068) - "WebSocket /ws/70070018?is_audio=true" [accepted]
Client #70070018 connected, audio mode: true
INFO: connection open
INFO: 127.0.0.1:50061 - "GET /static/js/pcm-player-processor.js HTTP/1.1" 200 OK
INFO: 127.0.0.1:50060 - "GET /static/js/pcm-recorder-processor.js HTTP/1.1" 200 OK
[AGENT TO CLIENT]: audio/pcm: 9600 bytes.
INFO: 127.0.0.1:50082 - "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 Not Found
[AGENT TO CLIENT]: audio/pcm: 11520 bytes.
[AGENT TO CLIENT]: audio/pcm: 11520 bytes.
如果你开发自己的流应用,这些控制台日志非常重要。在许多情况下,浏览器和服务器之间的通信失败是流应用 bug 的主要原因。
-
故障排除技巧
-
当
ws://不工作时: 如果你在 Chrome DevTools 上看到与ws://连接相关的任何错误,请尝试在app/static/js/app.js第 28 行将ws://替换为wss://。当你在云环境中运行示例并使用代理连接从浏览器连接时,可能会发生这种情况。 - 当模型不工作时: 如果你在应用服务器控制台上看到与模型可用性相关的任何错误,请尝试通过取消注释
.env文件中的#DEMO_AGENT_MODEL=gemini-2.0-flash-exp行并注释掉当前的DEMO_AGENT_MODEL行来使用备用模型。
4. 服务器代码概述¶
This server application enables real-time, streaming interaction with an ADK agent via WebSockets. Clients send text/audio to the ADK agent and receive streamed text/audio responses.
核心功能:
架构概述¶
以下图表说明了此流式传输应用中组件如何交互:
sequenceDiagram
participant Browser
participant FastAPI
participant ADK Runner
participant Gemini Live API
Note over Browser,Gemini Live API: 连接建立
Browser->>FastAPI: WebSocket 连接
FastAPI->>ADK Runner: start_agent_session()
ADK Runner->>Gemini Live API: 建立实时会话
Gemini Live API-->>ADK Runner: 会话就绪
Note over Browser,Gemini Live API: 双向通信
Browser->>FastAPI: 发送文本/音频消息
FastAPI->>ADK Runner: send_content() / send_realtime()
ADK Runner->>Gemini Live API: 转发到模型
Gemini Live API-->>ADK Runner: 流响应 (live_events)
ADK Runner-->>FastAPI: 处理事件
FastAPI-->>Browser: 发送响应 (文本/音频)
Note over Browser,Gemini Live API: 持续流式传输
loop 直到断开连接
Browser->>FastAPI: 附加消息
FastAPI->>ADK Runner: 处理输入
ADK Runner->>Gemini Live API: 转发
Gemini Live API-->>Browser: 流响应
end关键组件: - 浏览器: 发送/接收文本和音频数据的 WebSocket 客户端 - FastAPI: 处理 WebSocket 连接和路由消息的服务器 - ADK Runner: 管理智能体会话并与 Gemini Live API 协调 - Gemini Live API: 处理请求并流式传输响应(文本/音频)
ADK 流式传输设置¶
import os
import json
import asyncio
import base64
import warnings
from pathlib import Path
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# 在导入智能体之前加载环境变量
load_dotenv()
from google.genai import types
from google.genai.types import (
Part,
Content,
Blob,
)
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.agents import LiveRequestQueue
from google.adk.agents.run_config import RunConfig, StreamingMode
from google.adk.sessions.in_memory_session_service import InMemorySessionService
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
from fastapi.responses import FileResponse
from fastapi.websockets import WebSocketDisconnect
from google_search_agent.agent import root_agent
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=UserWarning, module="pydantic")
- 导入: 包括标准 Python 库(
os、json、asyncio、base64、warnings),dotenv用于环境变量,Google ADK(types、Part、Content、Blob、Runner、LiveRequestQueue、RunConfig、StreamingMode、InMemorySessionService),以及 FastAPI(FastAPI、WebSocket、StaticFiles、FileResponse、WebSocketDisconnect)。 load_dotenv(): 在导入 dotenv 后和 导入智能体之前 立即调用。这确保环境变量(如DEMO_AGENT_MODEL)在智能体模块初始化时可用。warnings.filterwarnings(): 抑制 Pydantic UserWarnings 以减少开发过程中的控制台噪音。
初始化:
#
# ADK Streaming
#
# 应用程序配置
APP_NAME = "adk-streaming-ws"
# 初始化会话服务
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
# APP_NAME 和 session_service 在上面的初始化部分中定义
runner = Runner(
app_name=APP_NAME,
agent=root_agent,
session_service=session_service,
)
APP_NAME: ADK 的应用程序标识符。session_service = InMemorySessionService(): 初始化内存 ADK 会话服务,适用于单实例或开发使用。生产环境可能使用持久化存储。runner = Runner(...): 在 模块级别创建 Runner 实例(生产就绪模式)。这为所有连接重用相同的 runner,提高性能和资源利用率。
start_agent_session(user_id, is_audio=False)¶
async def start_agent_session(user_id, is_audio=False):
"""启动智能体会话"""
# Get or create session (recommended pattern for production)
session_id = f"{APP_NAME}_{user_id}"
session = await runner.session_service.get_session(
app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
)
if not session:
session = await runner.session_service.create_session(
app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
)
# Configure response format based on client preference
# IMPORTANT: You must choose exactly ONE modality per session
# Either ["TEXT"] for text responses OR ["AUDIO"] for voice responses
# You cannot use both modalities simultaneously in the same session
# Force AUDIO modality for native audio models regardless of client preference
model_name = root_agent.model if isinstance(root_agent.model, str) else root_agent.model.model
is_native_audio = "native-audio" in model_name.lower()
modality = "AUDIO" if (is_audio or is_native_audio) else "TEXT"
# Enable session resumption for improved reliability
# For audio mode, enable output transcription to get text for UI display
run_config = RunConfig(
streaming_mode=StreamingMode.BIDI,
response_modalities=[modality],
session_resumption=types.SessionResumptionConfig(),
output_audio_transcription=types.AudioTranscriptionConfig() if (is_audio or is_native_audio) else None,
)
# Create LiveRequestQueue in async context (recommended best practice)
# This ensures the queue uses the correct event loop
live_request_queue = LiveRequestQueue()
# Start streaming session - returns async iterator for agent responses
live_events = runner.run_live(
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session.id,
live_request_queue=live_request_queue,
run_config=run_config,
)
return live_events, live_request_queue
This function initializes an ADK agent live session. It uses APP_NAME and session_service which are defined in the Initialization section above.
| 参数 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
user_id |
str |
唯一的客户端标识符。 |
is_audio |
bool |
True 为音频响应,False 为文本(默认)。 |
关键步骤:
1. 获取或创建会话: 尝试检索现有会话,如果不存在则创建新会话。此模式支持会话持久化和恢复。
2. 检测原生音频模型: 检查智能体的模型名称是否包含 "native-audio" 以自动为原生音频模型强制执行 AUDIO 模态。
3. 配置响应模态: 如果 is_audio=True 或模型是原生音频模型,则将模态设置为 "AUDIO",否则为 "TEXT"。注意:你必须为每个会话选择恰好一个模态。
4. 启用会话恢复: 配置 session_resumption=types.SessionResumptionConfig() 以在网络中断期间提高可靠性。
5. 启用输出转录(音频模式): 使用音频模式或原生音频模型时,启用 output_audio_transcription 以为 UI 显示获取音频响应的文本表示。
6. 创建 LiveRequestQueue: 在异步上下文中创建队列(最佳实践),用于将客户端输入发送到智能体。
7. 启动智能体会话: 调用 runner.run_live(...) 启动流式会话,返回 live_events(用于智能体响应的异步迭代器)和 live_request_queue。
- 创建 Runner: 为
root_agent实例化 ADK 运行器。 - 创建会话: 建立 ADK 会话。
- 设置响应模态: 将智能体响应配置为 "AUDIO" 或 "TEXT"。
- 创建 LiveRequestQueue: 为客户端输入到智能体创建队列。
- 启动智能体会话:
runner.run_live(...)启动智能体,返回:live_events:智能体事件的异步可迭代对象(文本、音频、完成)。live_request_queue:向智能体发送数据的队列。
输出音频转录¶
使用音频模式(is_audio=True)或原生音频模型(is_native_audio=True)时,应用程序通过 RunConfig 启用输出音频转录:
output_audio_transcription=types.AudioTranscriptionConfig() if (is_audio or is_native_audio) else None,
音频转录功能:
- 原生音频模型支持 - 与具有原生音频输出功能的模型配合工作
- 文本表示 - 为 UI 显示提供音频响应的文本转录
- 双重输出 - 同时启用音频播放和文本可视化
- 增强的可访问性 - 允许用户在听智能体说话的同时看到内容
用例:
- 在 UI 中将音频响应显示为文本以获得更好的用户体验
- 为喜欢文本的用户启用可访问性功能
- 通过记录智能体说的内容来支持调试
- 与音频一起创建对话记录
注意: 此功能需要支持输出音频转录的模型。并非所有 Live API 模型都支持此功能。
会话恢复配置¶
会话恢复配置¶
此示例应用在 RunConfig 中默认启用会话恢复:
run_config = RunConfig(
streaming_mode=StreamingMode.BIDI,
response_modalities=[modality],
session_resumption=types.SessionResumptionConfig()
)
会话恢复功能¶
- 自动句柄缓存 - 系统在实时对话期间自动缓存会话恢复句柄
- 透明重连 - 当连接中断时,系统尝试使用缓存的句柄恢复
- 上下文保持 - 对话上下文和状态在重连过程中得到保持
- 网络弹性 - 在不稳定的网络条件下提供更好的用户体验
实现说明¶
- 会话恢复句柄由 ADK 框架内部管理
- 不需要额外的客户端代码更改
- 此功能对长时间运行的流对话特别有益
- 连接中断对用户体验的干扰更小
禁用会话恢复(可选)¶
如果你在会话恢复时遇到错误或想禁用它:
- 检查模型兼容性 - 确保你使用支持会话恢复的模型
- API 限制 - 某些会话恢复功能可能不适用于所有 API 版本
- 禁用会话恢复 - 你可以通过从
RunConfig中移除session_resumption参数来禁用会话恢复:
# 禁用会话恢复
run_config = RunConfig(
streaming_mode=StreamingMode.BIDI,
response_modalities=[modality]
)
Now that we've covered session initialization and optional enhancements, let's explore the core messaging functions that handle bidirectional communication between the client and the ADK agent.
agent_to_client_messaging(websocket, live_events)¶
async def agent_to_client_messaging(websocket, live_events):
"""智能体到客户端通信"""
try:
async for event in live_events:
# Handle output audio transcription for native audio models
# This provides text representation of audio output for UI display
if event.output_transcription and event.output_transcription.text:
transcript_text = event.output_transcription.text
message = {
"mime_type": "text/plain",
"data": transcript_text,
"is_transcript": True
}
await websocket.send_text(json.dumps(message))
print(f"[AGENT TO CLIENT]: audio transcript: {transcript_text}")
# Continue to process audio data if present
# Don't return here as we may want to send both transcript and audio
# Read the Content and its first Part
part: Part = (
event.content and event.content.parts and event.content.parts[0]
)
if part:
# Audio data must be Base64-encoded for JSON transport
is_audio = part.inline_data and part.inline_data.mime_type.startswith("audio/pcm")
if is_audio:
audio_data = part.inline_data and part.inline_data.data
if audio_data:
message = {
"mime_type": "audio/pcm",
"data": base64.b64encode(audio_data).decode("ascii")
}
await websocket.send_text(json.dumps(message))
print(f"[AGENT TO CLIENT]: audio/pcm: {len(audio_data)} bytes.")
# If it's text and a partial text, send it (for cascade audio models or text mode)
if part.text and event.partial:
message = {
"mime_type": "text/plain",
"data": part.text
}
await websocket.send_text(json.dumps(message))
print(f"[AGENT TO CLIENT]: text/plain: {message}")
# If the turn complete or interrupted, send it
if event.turn_complete or event.interrupted:
message = {
"turn_complete": event.turn_complete,
"interrupted": event.interrupted,
}
await websocket.send_text(json.dumps(message))
print(f"[AGENT TO CLIENT]: {message}")
except WebSocketDisconnect:
print("Client disconnected from agent_to_client_messaging")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error in agent_to_client_messaging: {e}")
此异步函数将 ADK 智能体事件流式传输到 WebSocket 客户端。
Logic:
1. Iterates through live_events from the agent.
2. Audio Transcription (Native Audio Models): If the event contains output audio transcription text, sends it to the client with an is_transcript flag: { "mime_type": "text/plain", "data": "<transcript_text>", "is_transcript": True }. This enables displaying the audio content as text in the UI.
3. Content Processing:
* Extracts the first Part from event content (if it exists).
* Audio Data: If audio (PCM), Base64 encodes and sends it as JSON: { "mime_type": "audio/pcm", "data": "<base64_audio>" }.
* Text Data (Cascade Audio Models or Text Mode): If partial text, sends it as JSON: { "mime_type": "text/plain", "data": "<partial_text>" }.
4. Turn Completion/Interruption: Sends status flags to the client at the end of each event (see explanation below).
5. Logs messages.
Understanding Turn Completion and Interruption Events:
These events are critical for managing bidirectional streaming conversations:
turn_complete: Signals that the agent has finished generating a complete response. This event:- Marks the end of the agent's response turn
- Allows the UI to prepare for the next conversation turn
- Helps manage conversation state and flow
-
In the UI: Resets
currentMessageIdtonullso the next agent response creates a new message element -
interrupted: Signals that the agent's response was interrupted (e.g., when the user starts speaking during the agent's audio response). This event: - Indicates the current agent turn was cut short
- Enables natural conversation flow where users can interrupt the agent
- In the UI: Stops audio playback immediately by sending
{ command: "endOfAudio" }to the audio player worklet - Prevents the agent from continuing to speak while the user is talking
Both events are handled silently in the UI without visual indicators, prioritizing a seamless conversational experience.
client_to_agent_messaging(websocket, live_request_queue)¶
async def client_to_agent_messaging(websocket, live_request_queue):
"""客户端到智能体通信"""
try:
while True:
message_json = await websocket.receive_text()
message = json.loads(message_json)
mime_type = message["mime_type"]
data = message["data"]
if mime_type == "text/plain":
# send_content() sends text in "turn-by-turn mode"
# This signals a complete turn to the model, triggering immediate response
content = Content(role="user", parts=[Part.from_text(text=data)])
live_request_queue.send_content(content=content)
print(f"[CLIENT TO AGENT]: {data}")
elif mime_type == "audio/pcm":
# send_realtime() sends audio in "realtime mode"
# Data flows continuously without turn boundaries, enabling natural conversation
# Audio is Base64-encoded for JSON transport, decode before sending
decoded_data = base64.b64decode(data)
live_request_queue.send_realtime(Blob(data=decoded_data, mime_type=mime_type))
else:
raise ValueError(f"Mime type not supported: {mime_type}")
except WebSocketDisconnect:
print("Client disconnected from client_to_agent_messaging")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error in client_to_agent_messaging: {e}")
此异步函数将来自 WebSocket 客户端的消息转发给 ADK 智能体。
逻辑:
Error Handling:
Both agent_to_client_messaging and client_to_agent_messaging functions include try-except blocks to handle WebSocket disconnections gracefully:
WebSocketDisconnect: Catches when the client disconnects unexpectedly and logs the disconnection without raising an error- Generic
Exception: Catches any other errors (JSON parsing, Base64 decoding, etc.) and logs them for debugging
This error handling ensures:
- Clean shutdown when clients disconnect
- Proper logging for debugging connection issues
- The WebSocket connection closes gracefully without propagating unhandled exceptions
- The FIRST_EXCEPTION condition in asyncio.wait() can still trigger for cleanup
For production environments, consider additional error handling: - Send error messages back to the client to inform them of invalid input (before the connection closes) - Implement retry logic for transient failures - Add monitoring and alerting for error patterns - Validate message structure before processing to provide better error messages
FastAPI Web Application¶
#
# FastAPI web app
#
app = FastAPI()
STATIC_DIR = Path("static")
app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory=STATIC_DIR), name="static")
@app.get("/")
async def root():
"""提供 index.html"""
return FileResponse(os.path.join(STATIC_DIR, "index.html"))
@app.websocket("/ws/{user_id}")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket, user_id: int, is_audio: str):
"""Client websocket endpoint
This async function creates the LiveRequestQueue in an async context,
which is the recommended best practice from the ADK documentation.
This ensures the queue uses the correct event loop.
"""
await websocket.accept()
print(f"Client #{user_id} connected, audio mode: {is_audio}")
user_id_str = str(user_id)
live_events, live_request_queue = await start_agent_session(user_id_str, is_audio == "true")
# Run bidirectional messaging concurrently
agent_to_client_task = asyncio.create_task(
agent_to_client_messaging(websocket, live_events)
)
client_to_agent_task = asyncio.create_task(
client_to_agent_messaging(websocket, live_request_queue)
)
try:
# Wait for either task to complete (connection close or error)
tasks = [agent_to_client_task, client_to_agent_task]
done, pending = await asyncio.wait(tasks, return_when=asyncio.FIRST_EXCEPTION)
# Check for errors in completed tasks
for task in done:
if task.exception() is not None:
print(f"Task error for client #{user_id}: {task.exception()}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exception(type(task.exception()), task.exception(), task.exception().__traceback__)
finally:
# Clean up resources (always runs, even if asyncio.wait fails)
live_request_queue.close()
print(f"Client #{user_id} disconnected")
app = FastAPI(): 初始化应用程序。- 静态文件: 从
static目录提供文件,路径为/static。 @app.get("/")(根端点): 提供index.html。@app.websocket("/ws/{user_id}")(WebSocket 端点):- 路径参数:
user_id(int) 和is_audio(str: "true"/"false")。 - 连接处理:
- 接受 WebSocket 连接。
- 使用
user_id和is_audio调用start_agent_session()。 - 并发消息任务: 使用
asyncio.wait创建并运行agent_to_client_messaging和client_to_agent_messaging并发任务。这些任务处理双向消息流。 - 错误处理: 使用 try-finally 块:
- 检查已完成任务中的异常并使用 traceback 记录详细的错误信息
- 在
finally块中始终调用live_request_queue.close()以进行适当的清理
- 记录客户端连接和断开连接。
- 路径参数:
工作原理(整体流程)¶
- 客户端连接到
ws://<server>/ws/<user_id>?is_audio=<true_or_false>。 - 服务器的
websocket_endpoint接受,启动 ADK 会话(start_agent_session)。 - 两个
asyncio任务管理通信:client_to_agent_messaging:客户端 WebSocket 消息 -> ADKlive_request_queue。agent_to_client_messaging:ADKlive_events-> 客户端 WebSocket。
- 双向流式传输持续进行,直到断开连接或错误。
5. 客户端代码概述¶
JavaScript app.js (在 app/static/js 中) 管理与 ADK Streaming WebSocket 服务器的客户端交互。它处理发送文本/音频和接收/显示流式响应。
关键功能: 1. 管理 WebSocket 连接。 2. 处理文本输入。 3. 捕获麦克风音频(Web Audio API,AudioWorklets)。 4. 向服务器发送文本/音频。 5. 从 ADK 智能体接收和呈现文本/音频响应。 6. 管理 UI。
- 管理 WebSocket 连接。
- 处理文本输入。
- 捕获麦克风音频(Web Audio API,AudioWorklets)。
- 向后端发送文本/音频。
- 接收和渲染文本/音频智能体响应。
- 管理 UI。
前提条件¶
- HTML 结构: 需要特定的元素 ID(例如
messageForm、message、messages、sendButton、startAudioButton)。 - 后端服务器: Python FastAPI 服务器必须运行。
- 音频工作节点文件: 用于音频处理的
audio-player.js和audio-recorder.js。
WebSocket 处理¶
// 使用 WebSocket 连接连接服务器
const sessionId = Math.random().toString().substring(10);
const ws_url =
"ws://" + window.location.host + "/ws/" + sessionId;
let websocket = null;
let is_audio = false;
// 获取 DOM 元素
const messageForm = document.getElementById("messageForm");
const messageInput = document.getElementById("message");
const messagesDiv = document.getElementById("messages");
let currentMessageId = null;
// WebSocket 处理程序
function connectWebsocket() {
// 连接 websocket
websocket = new WebSocket(ws_url + "?is_audio=" + is_audio);
// 处理连接打开
websocket.onopen = function () {
// 连接打开消息
console.log("WebSocket connection opened.");
document.getElementById("messages").textContent = "Connection opened";
// 启用发送按钮
document.getElementById("sendButton").disabled = false;
addSubmitHandler();
};
// 处理传入消息
websocket.onmessage = function (event) {
// 解析传入消息
const message_from_server = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log("[AGENT TO CLIENT] ", message_from_server);
// 检查轮次是否完成
// 如果轮次完成,添加新消息
if (
message_from_server.turn_complete &&
message_from_server.turn_complete == true
) {
currentMessageId = null;
return;
}
// Check for interrupt message
if (
message_from_server.interrupted &&
message_from_server.interrupted === true
) {
// Stop audio playback if it's playing
if (audioPlayerNode) {
audioPlayerNode.port.postMessage({ command: "endOfAudio" });
}
return;
}
// If it's audio, play it
if (message_from_server.mime_type == "audio/pcm" && audioPlayerNode) {
audioPlayerNode.port.postMessage(base64ToArray(message_from_server.data));
}
// 如果是文本,打印它
if (message_from_server.mime_type == "text/plain") {
// 为新轮次添加新消息
if (currentMessageId == null) {
currentMessageId = Math.random().toString(36).substring(7);
const message = document.createElement("p");
message.id = currentMessageId;
// 将消息元素附加到 messagesDiv
messagesDiv.appendChild(message);
}
// 将消息文本添加到现有消息元素
const message = document.getElementById(currentMessageId);
message.textContent += message_from_server.data;
// 向下滚动到 messagesDiv 底部
messagesDiv.scrollTop = messagesDiv.scrollHeight;
}
};
// 处理连接关闭
websocket.onclose = function () {
console.log("WebSocket connection closed.");
document.getElementById("sendButton").disabled = true;
document.getElementById("messages").textContent = "Connection closed";
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("Reconnecting...");
connectWebsocket();
}, 5000);
};
websocket.onerror = function (e) {
console.log("WebSocket error: ", e);
};
}
connectWebsocket();
// 向表单添加提交处理程序
function addSubmitHandler() {
messageForm.onsubmit = function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
const message = messageInput.value;
if (message) {
const p = document.createElement("p");
p.textContent = "> " + message;
messagesDiv.appendChild(p);
messageInput.value = "";
sendMessage({
mime_type: "text/plain",
data: message,
});
console.log("[CLIENT TO AGENT] " + message);
}
return false;
};
}
// 向服务器发送消息作为 JSON 字符串
function sendMessage(message) {
if (websocket && websocket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
const messageJson = JSON.stringify(message);
websocket.send(messageJson);
}
}
// 将 Base64 数据解码为数组
function base64ToArray(base64) {
const binaryString = window.atob(base64);
const len = binaryString.length;
const bytes = new Uint8Array(len);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
bytes[i] = binaryString.charCodeAt(i);
}
return bytes.buffer;
}
- 连接设置: 生成
sessionId,构造ws_url。is_audio标志(初始为false)在激活时将?is_audio=true附加到 URL。connectWebsocket()初始化连接。 websocket.onopen: 启用发送按钮,更新 UI,调用addSubmitHandler()。websocket.onmessage: 解析来自服务器的传入 JSON。- 轮次完成: 当智能体轮次完成时,将
currentMessageId重置为null,为下一个响应做准备。 - 中断: 当智能体被中断(例如,用户在智能体音频响应期间开始说话)时,通过向
audioPlayerNode发送{ command: "endOfAudio" }停止音频播放。 - 音频数据 (
audio/pcm): 解码 Base64 音频(base64ToArray())并发送到audioPlayerNode进行播放。 - 文本数据 (
text/plain): 如果是新轮次(currentMessageId为 null),创建新的<p>。为流式效果将接收到的文本追加到当前消息段落。滚动messagesDiv。
- 轮次完成: 当智能体轮次完成时,将
websocket.onclose: 禁用发送按钮,更新 UI,5 秒后尝试自动重连。websocket.onerror: 记录错误。- 初始连接: 在脚本加载时调用
connectWebsocket()。
DOM 交互和消息提交¶
- 元素检索: 获取所需的 DOM 元素。
addSubmitHandler():附加到messageForm的提交。阻止默认提交,从messageInput获取文本,显示用户消息,清除输入,并使用{ mime_type: "text/plain", data: messageText }调用sendMessage()。sendMessage(messagePayload):如果 WebSocket 打开,发送 JSON 字符串化的messagePayload。
音频处理¶
let audioPlayerNode;
let audioPlayerContext;
let audioRecorderNode;
let audioRecorderContext;
let micStream;
// 导入音频工作节点
import { startAudioPlayerWorklet } from "./audio-player.js";
import { startAudioRecorderWorklet } from "./audio-recorder.js";
// 启动音频
function startAudio() {
// 启动音频输出
startAudioPlayerWorklet().then(([node, ctx]) => {
audioPlayerNode = node;
audioPlayerContext = ctx;
});
// 启动音频输入
startAudioRecorderWorklet(audioRecorderHandler).then(
([node, ctx, stream]) => {
audioRecorderNode = node;
audioRecorderContext = ctx;
micStream = stream;
}
);
}
// 仅当用户点击按钮时启动音频
// (由于 Web Audio API 的手势要求)
const startAudioButton = document.getElementById("startAudioButton");
startAudioButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
startAudioButton.disabled = true;
startAudio();
is_audio = true;
connectWebsocket(); // 以音频模式重新连接
});
// 音频录制器处理程序
function audioRecorderHandler(pcmData) {
// 以 base64 发送 pcm 数据
sendMessage({
mime_type: "audio/pcm",
data: arrayBufferToBase64(pcmData),
});
console.log("[CLIENT TO AGENT] sent %s bytes", pcmData.byteLength);
}
// 使用 Base64 编码数组缓冲区
function arrayBufferToBase64(buffer) {
let binary = "";
const bytes = new Uint8Array(buffer);
const len = bytes.byteLength;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
binary += String.fromCharCode(bytes[i]);
}
return window.btoa(binary);
}
- 音频工作节点: 通过
audio-player.js(用于播放)和audio-recorder.js(用于捕获)使用AudioWorkletNode。 - 状态变量: 存储 AudioContext 和 WorkletNode(例如
audioPlayerNode)。 startAudio():初始化播放器和录制器工作节点。将audioRecorderHandler作为回调传递给录制器。- "Start Audio" 按钮(
startAudioButton): - Web Audio API 需要用户手势。
- 点击时:禁用按钮,调用
startAudio(),设置is_audio = true,然后调用connectWebsocket()以音频模式重新连接(URL 包含?is_audio=true)。 audioRecorderHandler(pcmData):来自录制器工作节点的回调,包含 PCM 音频块。将pcmData编码为 Base64(arrayBufferToBase64())并通过带有mime_type: "audio/pcm"的sendMessage()发送到服务器。- 辅助函数:
base64ToArray()(服务器音频 -> 客户端播放器)和arrayBufferToBase64()(客户端麦克风音频 -> 服务器)。
工作原理(客户端流程)¶
- 页面加载: 在文本模式下建立 WebSocket。
- 文本交互: 用户输入/提交文本;发送到服务器。显示服务器文本响应,流式传输。
- 切换到音频模式: "Start Audio" 按钮点击初始化音频工作节点,设置
is_audio=true,并在音频模式下重新连接 WebSocket。 - 音频交互: 录制器向服务器发送麦克风音频(Base64 PCM)。服务器音频/文本响应由
websocket.onmessage处理,用于播放/显示。 - 连接管理: WebSocket 关闭时自动重连。
总结¶
本文概述了使用 ADK Streaming 和 FastAPI 构建的自定义异步 web 应用的服务器和客户端代码,实现实时、双向语音和文本通信。
本文概述了使用 ADK Streaming 和 FastAPI 构建的自定义异步 web 应用的服务器和客户端代码,实现双向语音和文本实时通信。
Python FastAPI 服务器代码初始化 ADK 智能体会话,配置为文本或音频响应。它使用 WebSocket 端点处理客户端连接。异步任务管理双向消息传递:将客户端文本或 Base64 编码的 PCM 音频转发到 ADK 智能体,以及将文本或 Base64 编码的 PCM 音频响应从 ADK 智能体流式传输回客户端。
生产环境的后续步骤¶
附加资源¶
有关 ADK 双向流式传输最佳实践、架构模式和高级功能的全面指导,请参阅:
- ADK 文档: 完整的 ADK 文档,包括智能体、工具和会话管理
- Gemini Live API 文档: Google AI Studio 的 Live API 参考
- Vertex AI Live API 文档: Google Cloud Vertex AI 的 Live API 参考
这些资源提供了以下详细说明:
- 基于阶段的生命周期模式 用于流式应用(初始化、会话管理、活动流式传输、终止)
- 事件处理模式,包括部分/完整文本、中断和轮次完成信号
- 高级功能,如会话恢复、语音活动检测、音频转录和上下文窗口压缩
- 生产部署策略,包括负载均衡、无状态会话管理和健康检查