ADK 自定义工具¶
在 ADK 智能体工作流中,工具是具有结构化输入和输出的编程函数,可以被 ADK 智能体调用以执行操作。ADK 工具的功能类似于你使用 函数调用 与 Gemini 或其他生成式 AI 模型的方式。你可以使用 ADK 工具执行各种操作和编程功能,例如:
- 查询数据库
- 发出 API 请求:获取天气数据、预订系统
- 搜索网络
- 执行代码片段
- 从文档中检索信息(RAG)
- 与其他软件或服务交互
什么是工具?¶
在 ADK 上下文中,工具代表提供给 AI 智能体的特定能力,使其能够执行操作并与超出其核心文本生成和推理能力的世界交互。使有能力的智能体与基本语言模型区别开来的是它们对工具的有效使用。
从技术上讲,工具通常是一个模块化代码组件——类似于 Python/Java函数、类方法,甚至是另一个专业智能体——设计用于执行不同的、预定义的任务。这些任务通常涉及与外部系统或数据交互。
关键特性¶
面向行动: 工具为智能体执行特定操作,例如搜索信息、调用 API 或执行计算。
扩展智能体能力: 它们使智能体能够访问实时信息、影响外部系统,并克服其训练数据中固有的知识限制。
执行预定义逻辑: 重要的是,工具执行特定的、开发者定义的逻辑。它们不像智能体的核心大语言模型(LLM)那样具有自己独立的推理能力。LLM 推理使用哪个工具、何时使用以及使用什么输入,但工具本身只是执行其指定的功能。
智能体如何使用工具¶
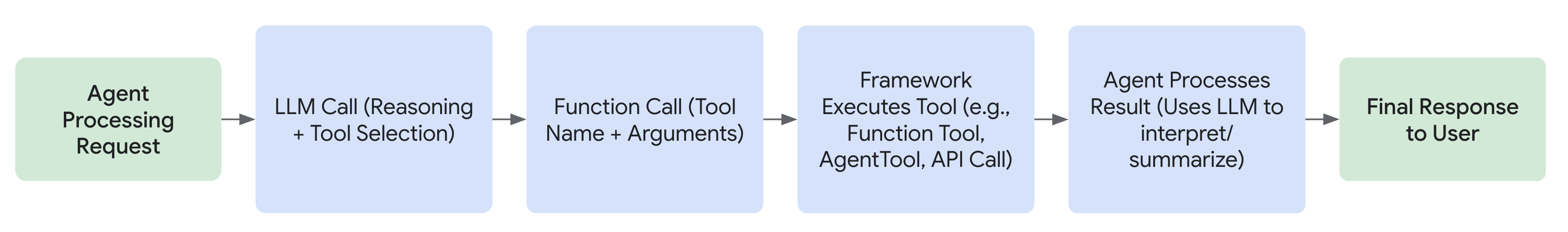
智能体通过通常涉及函数调用的机制动态利用工具。该过程通常遵循以下步骤:
- 推理: 智能体的 LLM 分析其系统指令、对话历史和用户请求。
- 选择: 基于分析,LLM 决定执行哪个工具(如果有),基于智能体可用的工具和描述每个工具的文档字符串。
- 调用: LLM 为所选工具生成所需的参数(输入)并触发其执行。
- 观察: 智能体接收工具返回的输出(结果)。
- 完成: 智能体将工具的输出纳入其持续的推理过程,以制定下一个响应、决定后续步骤或确定目标是否已达成。
将工具视为智能体智能核心(LLM)可以按需访问和利用以完成复杂任务的专门工具包。
ADK 中的工具类型¶
ADK 通过支持多种类型的工具提供灵活性:
- 函数工具: 由你创建,专为你的特定应用程序需求定制。
- 内置工具: 框架提供的现成工具,用于常见任务。 示例:Google 搜索、代码执行、检索增强生成(RAG)。
- 第三方工具: 从流行的外部库无缝集成工具。
导航到上面链接的相关文档页面,获取每种工具类型的详细信息和示例。
在智能体指令中引用工具¶
在智能体的指令中,你可以通过使用其 函数名称 直接引用工具。如果工具的 函数名称 和 文档字符串 足够描述性,你的指令可以主要关注 大语言模型(LLM)应该何时使用工具。这促进了清晰性并帮助模型理解每个工具的预期用途。
清楚地指示智能体如何处理工具可能产生的不同返回值 是至关重要的。 例如,如果工具返回错误消息,你的指令应指定智能体是应该重试操作、放弃任务,还是向用户请求额外信息。
此外,ADK 支持工具的顺序使用,其中一个工具的输出可以作为另一个工具的输入。 在实现此类工作流时,重要的是在智能体的指令中 描述预期的工具使用顺序,以引导模型完成必要的步骤。
示例¶
以下示例展示了智能体如何通过 在其指令中引用其函数名称 来使用工具。 它还演示了如何引导智能体 处理来自工具的不同返回值,例如成功或错误消息,以及如何编排 顺序使用多个工具 来完成任务。
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import asyncio
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.genai import types
APP_NAME="weather_sentiment_agent"
USER_ID="user1234"
SESSION_ID="1234"
MODEL_ID="gemini-2.0-flash"
# Tool 1
def get_weather_report(city: str) -> dict:
"""Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.
Returns:
dict: A dictionary containing the weather information with a 'status' key ('success' or 'error') and a 'report' key with the weather details if successful, or an 'error_message' if an error occurred.
"""
if city.lower() == "london":
return {"status": "success", "report": "The current weather in London is cloudy with a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius and a chance of rain."}
elif city.lower() == "paris":
return {"status": "success", "report": "The weather in Paris is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius."}
else:
return {"status": "error", "error_message": f"Weather information for '{city}' is not available."}
weather_tool = FunctionTool(func=get_weather_report)
# Tool 2
def analyze_sentiment(text: str) -> dict:
"""Analyzes the sentiment of the given text.
Returns:
dict: A dictionary with 'sentiment' ('positive', 'negative', or 'neutral') and a 'confidence' score.
"""
if "good" in text.lower() or "sunny" in text.lower():
return {"sentiment": "positive", "confidence": 0.8}
elif "rain" in text.lower() or "bad" in text.lower():
return {"sentiment": "negative", "confidence": 0.7}
else:
return {"sentiment": "neutral", "confidence": 0.6}
sentiment_tool = FunctionTool(func=analyze_sentiment)
# Agent
weather_sentiment_agent = Agent(
model=MODEL_ID,
name='weather_sentiment_agent',
instruction="""You are a helpful assistant that provides weather information and analyzes the sentiment of user feedback.
**If the user asks about the weather in a specific city, use the 'get_weather_report' tool to retrieve the weather details.**
**If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns a 'success' status, provide the weather report to the user.**
**If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns an 'error' status, inform the user that the weather information for the specified city is not available and ask if they have another city in mind.**
**After providing a weather report, if the user gives feedback on the weather (e.g., 'That's good' or 'I don't like rain'), use the 'analyze_sentiment' tool to understand their sentiment.** Then, briefly acknowledge their sentiment.
You can handle these tasks sequentially if needed.""",
tools=[weather_tool, sentiment_tool]
)
async def main():
"""Main function to run the agent asynchronously."""
# Session and Runner Setup
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
# Use 'await' to correctly create the session
await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=weather_sentiment_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
# Agent Interaction
query = "weather in london?"
print(f"User Query: {query}")
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
# The runner's run method handles the async loop internally
events = runner.run(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response:", final_response)
# Standard way to run the main async function
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
/**
* Copyright 2025 Google LLC
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import { LlmAgent, FunctionTool, InMemoryRunner, isFinalResponse, stringifyContent } from "@google/adk";
import { z } from "zod";
import { Content, createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
/**
* Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.
*/
function getWeatherReport(params: { city: string }): Record<string, any> {
if (params.city.toLowerCase().includes("london")) {
return {
"status": "success",
"report": "The current weather in London is cloudy with a " +
"temperature of 18 degrees Celsius and a chance of rain.",
};
}
if (params.city.toLowerCase().includes("paris")) {
return {
"status": "success",
"report": "The weather in Paris is sunny with a temperature of 25 " +
"degrees Celsius.",
};
}
return {
"status": "error",
"error_message": `Weather information for '${params.city}' is not available.`,
};
}
/**
* Analyzes the sentiment of a given text.
*/
function analyzeSentiment(params: { text: string }): Record<string, any> {
if (params.text.includes("cloudy") || params.text.includes("rain")) {
return { "status": "success", "sentiment": "negative" };
}
if (params.text.includes("sunny")) {
return { "status": "success", "sentiment": "positive" };
}
return { "status": "success", "sentiment": "neutral" };
}
const weatherTool = new FunctionTool({
name: "get_weather_report",
description: "Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.",
parameters: z.object({
city: z.string().describe("The city to get the weather for."),
}),
execute: getWeatherReport,
});
const sentimentTool = new FunctionTool({
name: "analyze_sentiment",
description: "Analyzes the sentiment of a given text.",
parameters: z.object({
text: z.string().describe("The text to analyze the sentiment of."),
}),
execute: analyzeSentiment,
});
const instruction = `
You are a helpful assistant that first checks the weather and then analyzes
its sentiment.
Follow these steps:
1. Use the 'get_weather_report' tool to get the weather for the requested
city.
2. If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns an error, inform the user about
the error and stop.
3. If the weather report is available, use the 'analyze_sentiment' tool to
determine the sentiment of the weather report.
4. Finally, provide a summary to the user, including the weather report and
its sentiment.
`;
const agent = new LlmAgent({
name: "weather_sentiment_agent",
instruction: instruction,
tools: [weatherTool, sentimentTool],
model: "gemini-2.5-flash"
});
async function main() {
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({ agent: agent, appName: "weather_sentiment_app" });
await runner.sessionService.createSession({
appName: "weather_sentiment_app",
userId: "user1",
sessionId: "session1"
});
const newMessage: Content = createUserContent("What is the weather in London?");
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({
userId: "user1",
sessionId: "session1",
newMessage: newMessage,
})) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
const text = stringifyContent(event).trim();
if (text) {
console.log(text);
}
}
}
}
main();
// Copyright 2025 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool/functiontool"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
type getWeatherReportArgs struct {
City string `json:"city" jsonschema:"The city for which to get the weather report."`
}
type getWeatherReportResult struct {
Status string `json:"status"`
Report string `json:"report,omitempty"`
}
func getWeatherReport(ctx tool.Context, args getWeatherReportArgs) (getWeatherReportResult, error) {
if strings.ToLower(args.City) == "london" {
return getWeatherReportResult{Status: "success", Report: "The current weather in London is cloudy with a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius and a chance of rain."}, nil
}
if strings.ToLower(args.City) == "paris" {
return getWeatherReportResult{Status: "success", Report: "The weather in Paris is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius."}, nil
}
return getWeatherReportResult{}, fmt.Errorf("weather information for '%s' is not available.", args.City)
}
type analyzeSentimentArgs struct {
Text string `json:"text" jsonschema:"The text to analyze for sentiment."`
}
type analyzeSentimentResult struct {
Sentiment string `json:"sentiment"`
Confidence float64 `json:"confidence"`
}
func analyzeSentiment(ctx tool.Context, args analyzeSentimentArgs) (analyzeSentimentResult, error) {
if strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(args.Text), "good") || strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(args.Text), "sunny") {
return analyzeSentimentResult{Sentiment: "positive", Confidence: 0.8}, nil
}
if strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(args.Text), "rain") || strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(args.Text), "bad") {
return analyzeSentimentResult{Sentiment: "negative", Confidence: 0.7}, nil
}
return analyzeSentimentResult{Sentiment: "neutral", Confidence: 0.6}, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, "gemini-2.0-flash", &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
weatherTool, err := functiontool.New(
functiontool.Config{
Name: "get_weather_report",
Description: "Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.",
},
getWeatherReport,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
sentimentTool, err := functiontool.New(
functiontool.Config{
Name: "analyze_sentiment",
Description: "Analyzes the sentiment of the given text.",
},
analyzeSentiment,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
weatherSentimentAgent, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "weather_sentiment_agent",
Model: model,
Instruction: "You are a helpful assistant that provides weather information and analyzes the sentiment of user feedback. **If the user asks about the weather in a specific city, use the 'get_weather_report' tool to retrieve the weather details.** **If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns a 'success' status, provide the weather report to the user.** **If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns an 'error' status, inform the user that the weather information for the specified city is not available and ask if they have another city in mind.** **After providing a weather report, if the user gives feedback on the weather (e.g., 'That's good' or 'I don't like rain'), use the 'analyze_sentiment' tool to understand their sentiment.** Then, briefly acknowledge their sentiment. You can handle these tasks sequentially if needed.",
Tools: []tool.Tool{weatherTool, sentimentTool},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
runner, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: "weather_sentiment_agent",
Agent: weatherSentimentAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
session, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: "weather_sentiment_agent",
UserID: "user1234",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
run(ctx, runner, session.Session.ID(), "weather in london?")
run(ctx, runner, session.Session.ID(), "I don't like rain.")
}
func run(ctx context.Context, r *runner.Runner, sessionID string, prompt string) {
fmt.Printf("\n> %s\n", prompt)
events := r.Run(
ctx,
"user1234",
sessionID,
genai.NewContentFromText(prompt, genai.RoleUser),
agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeNone,
},
)
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ERROR during agent execution: %v", err)
}
if event.Content.Parts[0].Text != "" {
fmt.Printf("Agent Response: %s\n", event.Content.Parts[0].Text)
}
}
}
import com.google.adk.agents.BaseAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.runner.Runner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.InMemorySessionService;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.adk.tools.Annotations.Schema;
import com.google.adk.tools.FunctionTool;
import com.google.adk.tools.ToolContext; // Ensure this import is correct
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
public class WeatherSentimentAgentApp {
private static final String APP_NAME = "weather_sentiment_agent";
private static final String USER_ID = "user1234";
private static final String SESSION_ID = "1234";
private static final String MODEL_ID = "gemini-2.0-flash";
/**
* Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.
*
* @param city The city for which to retrieve the weather report.
* @param toolContext The context for the tool.
* @return A dictionary containing the weather information.
*/
public static Map<String, Object> getWeatherReport(
@Schema(name = "city")
String city,
@Schema(name = "toolContext")
ToolContext toolContext) {
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
if (city.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).equals("london")) {
response.put("status", "success");
response.put(
"report",
"The current weather in London is cloudy with a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius and a"
+ " chance of rain.");
} else if (city.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).equals("paris")) {
response.put("status", "success");
response.put(
"report", "The weather in Paris is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius.");
} else {
response.put("status", "error");
response.put(
"error_message", String.format("Weather information for '%s' is not available.", city));
}
return response;
}
/**
* Analyzes the sentiment of the given text.
*
* @param text The text to analyze.
* @param toolContext The context for the tool.
* @return A dictionary with sentiment and confidence score.
*/
public static Map<String, Object> analyzeSentiment(
@Schema(name = "text")
String text,
@Schema(name = "toolContext")
ToolContext toolContext) {
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
String lowerText = text.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
if (lowerText.contains("good") || lowerText.contains("sunny")) {
response.put("sentiment", "positive");
response.put("confidence", 0.8);
} else if (lowerText.contains("rain") || lowerText.contains("bad")) {
response.put("sentiment", "negative");
response.put("confidence", 0.7);
} else {
response.put("sentiment", "neutral");
response.put("confidence", 0.6);
}
return response;
}
/**
* Calls the agent with the given query and prints the final response.
*
* @param runner The runner to use.
* @param query The query to send to the agent.
*/
public static void callAgent(Runner runner, String query) {
Content content = Content.fromParts(Part.fromText(query));
InMemorySessionService sessionService = (InMemorySessionService) runner.sessionService();
Session session =
sessionService
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, /* state= */ null, SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
runner
.runAsync(session.userId(), session.id(), content)
.forEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse()
&& event.content().isPresent()
&& event.content().get().parts().isPresent()
&& !event.content().get().parts().get().isEmpty()
&& event.content().get().parts().get().get(0).text().isPresent()) {
String finalResponse = event.content().get().parts().get().get(0).text().get();
System.out.println("Agent Response: " + finalResponse);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
FunctionTool weatherTool =
FunctionTool.create(
WeatherSentimentAgentApp.class.getMethod(
"getWeatherReport", String.class, ToolContext.class));
FunctionTool sentimentTool =
FunctionTool.create(
WeatherSentimentAgentApp.class.getMethod(
"analyzeSentiment", String.class, ToolContext.class));
BaseAgent weatherSentimentAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.model(MODEL_ID)
.name("weather_sentiment_agent")
.description("Weather Sentiment Agent")
.instruction("""
You are a helpful assistant that provides weather information and analyzes the
sentiment of user feedback
**If the user asks about the weather in a specific city, use the
'get_weather_report' tool to retrieve the weather details.**
**If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns a 'success' status, provide the
weather report to the user.**
**If the 'get_weather_report' tool returns an 'error' status, inform the
user that the weather information for the specified city is not available
and ask if they have another city in mind.**
**After providing a weather report, if the user gives feedback on the
weather (e.g., 'That's good' or 'I don't like rain'), use the
'analyze_sentiment' tool to understand their sentiment.** Then, briefly
acknowledge their sentiment.
You can handle these tasks sequentially if needed.
""")
.tools(ImmutableList.of(weatherTool, sentimentTool))
.build();
InMemorySessionService sessionService = new InMemorySessionService();
Runner runner = new Runner(weatherSentimentAgent, APP_NAME, null, sessionService);
// Change the query to ensure the tool is called with a valid city that triggers a "success"
// response from the tool, like "london" (without the question mark).
callAgent(runner, "weather in paris");
}
}
Tool Context¶
对于更高级的场景,ADK 允许你通过包含特殊参数 tool_context: ToolContext 在你的工具函数中访问额外的上下文信息。通过在函数签名中包含此项,ADK 将在智能体执行期间调用你的工具时自动提供 ToolContext 类的实例。
ToolContext 提供对几个关键信息和控制杠杆的访问:
-
state: State: 读取和修改当前会话的状态。在此处进行的更改会被跟踪和持久化。 -
actions: EventActions: 影响工具运行后智能体的后续操作(例如,跳过摘要、转移到另一个智能体)。 -
function_call_id: str: 框架分配给此特定工具调用的唯一标识符。用于跟踪和与身份验证响应相关联。这在单个模型响应中调用多个工具时也很有用。 -
function_call_event_id: str: 此属性提供触发当前工具调用的事件的唯一标识符。这可用于跟踪和日志记录目的。 -
auth_response: Any: 如果在此工具调用之前完成了身份验证流程,则包含身份验证响应/凭据。 -
服务访问:与配置的服务(如制品和记忆)交互的方法。
请注意,你不应将 tool_context 参数包含在工具函数文档字符串中。由于 ToolContext 是在 LLM 决定调用工具函数之后由 ADK 框架自动注入的,因此它与 LLM 的决策无关,包含它可能会使 LLM 混淆。
状态管理¶
tool_context.state 属性提供对与当前会话关联的状态的直接读写访问。它的行为类似于字典,但确保任何修改都被跟踪为增量并由会话服务持久化。这使工具能够在不同交互和智能体步骤之间维护和共享信息。
-
读取状态: 使用标准字典访问(
tool_context.state['my_key'])或.get()方法(tool_context.state.get('my_key', default_value))。 -
写入状态: 直接分配值(
tool_context.state['new_key'] = 'new_value')。这些更改记录在结果事件的 state_delta 中。 -
状态前缀: 记住标准状态前缀:
-
app:*: 在应用程序的所有用户之间共享。 -
user:*: 对于当前用户的所有会话特定。 -
(无前缀):对于当前会话特定。
-
temp:*: 临时的,在调用之间不持久化(用于在单次运行调用内传递数据很有用,但在 LLM 调用之间操作的工具上下文中通常不太有用)。
-
from google.adk.tools import ToolContext, FunctionTool
def update_user_preference(preference: str, value: str, tool_context: ToolContext):
"""Updates a user-specific preference."""
user_prefs_key = "user:preferences"
# Get current preferences or initialize if none exist
preferences = tool_context.state.get(user_prefs_key, {})
preferences[preference] = value
# Write the updated dictionary back to the state
tool_context.state[user_prefs_key] = preferences
print(f"Tool: Updated user preference '{preference}' to '{value}'")
return {"status": "success", "updated_preference": preference}
pref_tool = FunctionTool(func=update_user_preference)
# In an Agent:
# my_agent = Agent(..., tools=[pref_tool])
# When the LLM calls update_user_preference(preference='theme', value='dark', ...):
# The tool_context.state will be updated, and the change will be part of the
# resulting tool response event's actions.state_delta.
import { ToolContext } from "@google/adk";
// Updates a user-specific preference.
export function updateUserThemePreference(
value: string,
toolContext: ToolContext
): Record<string, any> {
const userPrefsKey = "user:preferences";
// Get current preferences or initialize if none exist
const preferences = toolContext.state.get(userPrefsKey, {}) as Record<string, any>;
preferences["theme"] = value;
// Write the updated dictionary back to the state
toolContext.state.set(userPrefsKey, preferences);
console.log(
`Tool: Updated user preference ${userPrefsKey} to ${JSON.stringify(toolContext.state.get(userPrefsKey))}`
);
return {
status: "success",
updated_preference: toolContext.state.get(userPrefsKey),
};
// When the LLM calls updateUserThemePreference("dark"):
// The toolContext.state will be updated, and the change will be part of the
// resulting tool response event's actions.stateDelta.
}
import (
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
)
type updateUserPreferenceArgs struct {
Preference string `json:"preference" jsonschema:"The name of the preference to set."`
Value string `json:"value" jsonschema:"The value to set for the preference."`
}
type updateUserPreferenceResult struct {
UpdatedPreference string `json:"updated_preference"`
}
func updateUserPreference(ctx tool.Context, args updateUserPreferenceArgs) (*updateUserPreferenceResult, error) {
userPrefsKey := "user:preferences"
val, err := ctx.State().Get(userPrefsKey)
if err != nil {
val = make(map[string]any)
}
preferencesMap, ok := val.(map[string]any)
if !ok {
preferencesMap = make(map[string]any)
}
preferencesMap[args.Preference] = args.Value
if err := ctx.State().Set(userPrefsKey, preferencesMap); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Printf("Tool: Updated user preference '%s' to '%s'\n", args.Preference, args.Value)
return &updateUserPreferenceResult{
UpdatedPreference: args.Preference,
}, nil
}
import com.google.adk.tools.FunctionTool;
import com.google.adk.tools.ToolContext;
// 更新用户特定的偏好设置。
public Map<String, String> updateUserThemePreference(String value, ToolContext toolContext) {
String userPrefsKey = "user:preferences:theme";
// 获取当前偏好或如果不存在则初始化
String preference = toolContext.state().getOrDefault(userPrefsKey, "").toString();
if (preference.isEmpty()) {
preference = value;
}
// 将更新后的字典写回状态
toolContext.state().put("user:preferences", preference);
System.out.printf("工具:将用户偏好 %s 更新为 %s", userPrefsKey, preference);
return Map.of("status", "success", "updated_preference", toolContext.state().get(userPrefsKey).toString());
// 当 LLM 调用 updateUserThemePreference("dark") 时:
// toolContext.state 将被更新,更改将成为
// 结果工具响应事件的 actions.stateDelta 的一部分。
}
控制智能体流程¶
Python 和 TypeScript 中的 tool_context.actions 属性、Java 中的 ToolContext.actions() 和 Go 中的 tool.Context.Actions() 包含一个 EventActions 对象。修改此对象上的属性可让你的工具影响工具完成执行后智能体或框架执行的操作。
-
skip_summarization: bool: (默认值:False)如果设置为 True,指示 ADK 绕过通常总结工具输出的 LLM 调用。如果你的工具返回值已经是用户准备就绪的消息,这很有用。 -
transfer_to_agent: str: 将其设置为另一个智能体的名称。框架将停止当前智能体的执行并 将对话控制权转移给指定的智能体。这允许工具动态地将任务转交给更专业的智能体。 -
escalate: bool: (默认值:False)将此设置为 True 表示当前智能体无法处理请求并应将控制权传递给其父智能体(如果在层次结构中)。在 LoopAgent 中,在子智能体的工具中设置 escalate=True 将终止循环。
示例¶
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.adk.tools import ToolContext
from google.genai import types
APP_NAME="customer_support_agent"
USER_ID="user1234"
SESSION_ID="1234"
def check_and_transfer(query: str, tool_context: ToolContext) -> str:
"""Checks if the query requires escalation and transfers to another agent if needed."""
if "urgent" in query.lower():
print("Tool: Detected urgency, transferring to the support agent.")
tool_context.actions.transfer_to_agent = "support_agent"
return "Transferring to the support agent..."
else:
return f"Processed query: '{query}'. No further action needed."
escalation_tool = FunctionTool(func=check_and_transfer)
main_agent = Agent(
model='gemini-2.0-flash',
name='main_agent',
instruction="""You are the first point of contact for customer support of an analytics tool. Answer general queries. If the user indicates urgency, use the 'check_and_transfer' tool.""",
tools=[check_and_transfer]
)
support_agent = Agent(
model='gemini-2.0-flash',
name='support_agent',
instruction="""You are the dedicated support agent. Mentioned you are a support handler and please help the user with their urgent issue."""
)
main_agent.sub_agents = [support_agent]
# Session and Runner
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=main_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
return session, runner
# Agent Interaction
async def call_agent_async(query):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
session, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("this is urgent, i cant login")
/**
* Copyright 2025 Google LLC
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import { LlmAgent, FunctionTool, ToolContext, InMemoryRunner, isFinalResponse, stringifyContent } from "@google/adk";
import { z } from "zod";
import { Content, createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
function checkAndTransfer(
params: { query: string },
toolContext?: ToolContext
): Record<string, any> {
if (!toolContext) {
// This should not happen in a normal ADK flow where the tool is called by an agent.
throw new Error("ToolContext is required to transfer agents.");
}
if (params.query.toLowerCase().includes("urgent")) {
console.log("Tool: Urgent query detected, transferring to support_agent.");
toolContext.actions.transferToAgent = "support_agent";
return { status: "success", message: "Transferring to support agent." };
}
console.log("Tool: Query is not urgent, handling normally.");
return { status: "success", message: "Query will be handled by the main agent." };
}
const transferTool = new FunctionTool({
name: "check_and_transfer",
description: "Checks the user's query and transfers to a support agent if urgent.",
parameters: z.object({
query: z.string().describe("The user query to analyze."),
}),
execute: checkAndTransfer,
});
const supportAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: "support_agent",
description: "Handles urgent user requests about accounts.",
instruction: "You are the support agent. Handle the user's urgent request.",
model: "gemini-2.5-flash"
});
const mainAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: "main_agent",
description: "The main agent that routes non-urgent queries.",
instruction: "You are the main agent. Use the check_and_transfer tool to analyze the user query. If the query is not urgent, handle it yourself.",
tools: [transferTool],
subAgents: [supportAgent],
model: "gemini-2.5-flash"
});
async function main() {
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({ agent: mainAgent, appName: "customer_support_app" });
console.log("--- Running with a non-urgent query ---");
await runner.sessionService.createSession({ appName: "customer_support_app", userId: "user1", sessionId: "session1" });
const nonUrgentMessage: Content = createUserContent("I have a general question about my account.");
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({ userId: "user1", sessionId: "session1", newMessage: nonUrgentMessage })) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
const text = stringifyContent(event).trim();
if (text) {
console.log(`Final Response: ${text}`);
}
}
}
console.log("\n--- Running with an urgent query ---");
await runner.sessionService.createSession({ appName: "customer_support_app", userId: "user1", sessionId: "session2" });
const urgentMessage: Content = createUserContent("My account is locked and this is urgent!");
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({ userId: "user1", sessionId: "session2", newMessage: urgentMessage })) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
const text = stringifyContent(event).trim();
if (text) {
console.log(`Final Response: ${text}`);
}
}
}
}
main();
// Copyright 2025 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool/functiontool"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
type checkAndTransferArgs struct {
Query string `json:"query" jsonschema:"The user's query to check for urgency."`
}
type checkAndTransferResult struct {
Status string `json:"status"`
}
func checkAndTransfer(ctx tool.Context, args checkAndTransferArgs) (checkAndTransferResult, error) {
if strings.Contains(strings.ToLower(args.Query), "urgent") {
fmt.Println("Tool: Detected urgency, transferring to the support agent.")
ctx.Actions().TransferToAgent = "support_agent"
return checkAndTransferResult{Status: "Transferring to the support agent..."}, nil
}
return checkAndTransferResult{Status: fmt.Sprintf("Processed query: '%s'. No further action needed.", args.Query)}, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, "gemini-2.0-flash", &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
supportAgent, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "support_agent",
Model: model,
Instruction: "You are the dedicated support agent. Mentioned you are a support handler and please help the user with their urgent issue.",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
checkAndTransferTool, err := functiontool.New(
functiontool.Config{
Name: "check_and_transfer",
Description: "Checks if the query requires escalation and transfers to another agent if needed.",
},
checkAndTransfer,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
mainAgent, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "main_agent",
Model: model,
Instruction: "You are the first point of contact for customer support of an analytics tool. Answer general queries. If the user indicates urgency, use the 'check_and_transfer' tool.",
Tools: []tool.Tool{checkAndTransferTool},
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{supportAgent},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
runner, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: "customer_support_agent",
Agent: mainAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
session, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: "customer_support_agent",
UserID: "user1234",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
run(ctx, runner, session.Session.ID(), "this is urgent, i cant login")
}
func run(ctx context.Context, r *runner.Runner, sessionID string, prompt string) {
fmt.Printf("\n> %s\n", prompt)
events := r.Run(
ctx,
"user1234",
sessionID,
genai.NewContentFromText(prompt, genai.RoleUser),
agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeNone,
},
)
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ERROR during agent execution: %v", err)
}
if event.Content.Parts[0].Text != "" {
fmt.Printf("Agent Response: %s\n", event.Content.Parts[0].Text)
}
}
}
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.runner.Runner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.InMemorySessionService;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.adk.tools.Annotations.Schema;
import com.google.adk.tools.FunctionTool;
import com.google.adk.tools.ToolContext;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
public class CustomerSupportAgentApp {
private static final String APP_NAME = "customer_support_agent";
private static final String USER_ID = "user1234";
private static final String SESSION_ID = "1234";
private static final String MODEL_ID = "gemini-2.0-flash";
/**
* Checks if the query requires escalation and transfers to another agent if needed.
*
* @param query The user's query.
* @param toolContext The context for the tool.
* @return A map indicating the result of the check and transfer.
*/
public static Map<String, Object> checkAndTransfer(
@Schema(name = "query", description = "the user query")
String query,
@Schema(name = "toolContext", description = "the tool context")
ToolContext toolContext) {
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
if (query.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).contains("urgent")) {
System.out.println("Tool: Detected urgency, transferring to the support agent.");
toolContext.actions().setTransferToAgent("support_agent");
response.put("status", "transferring");
response.put("message", "Transferring to the support agent...");
} else {
response.put("status", "processed");
response.put(
"message", String.format("Processed query: '%s'. No further action needed.", query));
}
return response;
}
/**
* Calls the agent with the given query and prints the final response.
*
* @param runner The runner to use.
* @param query The query to send to the agent.
*/
public static void callAgent(Runner runner, String query) {
Content content =
Content.fromParts(Part.fromText(query));
InMemorySessionService sessionService = (InMemorySessionService) runner.sessionService();
// Fixed: session ID does not need to be an optional.
Session session =
sessionService
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, /* state= */ null, SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
runner
.runAsync(session.userId(), session.id(), content)
.forEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse()
&& event.content().isPresent()
&& event.content().get().parts().isPresent()
&& !event.content().get().parts().get().isEmpty()
&& event.content().get().parts().get().get(0).text().isPresent()) {
String finalResponse = event.content().get().parts().get().get(0).text().get();
System.out.println("Agent Response: " + finalResponse);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
FunctionTool escalationTool =
FunctionTool.create(
CustomerSupportAgentApp.class.getMethod(
"checkAndTransfer", String.class, ToolContext.class));
LlmAgent supportAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.model(MODEL_ID)
.name("support_agent")
.description("""
The dedicated support agent.
Mentions it is a support handler and helps the user with their urgent issue.
""")
.instruction("""
You are the dedicated support agent.
Mentioned you are a support handler and please help the user with their urgent issue.
""")
.build();
LlmAgent mainAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.model(MODEL_ID)
.name("main_agent")
.description("""
The first point of contact for customer support of an analytics tool.
Answers general queries.
If the user indicates urgency, uses the 'check_and_transfer' tool.
""")
.instruction("""
You are the first point of contact for customer support of an analytics tool.
Answer general queries.
If the user indicates urgency, use the 'check_and_transfer' tool.
""")
.tools(ImmutableList.of(escalationTool))
.subAgents(supportAgent)
.build();
// Fixed: LlmAgent.subAgents() expects 0 arguments.
// Sub-agents are now added to the main agent via its builder,
// as `subAgents` is a property that should be set during agent construction
// if it's not dynamically managed.
InMemorySessionService sessionService = new InMemorySessionService();
Runner runner = new Runner(mainAgent, APP_NAME, null, sessionService);
// Agent Interaction
callAgent(runner, "this is urgent, i cant login");
}
}
Explanation¶
- 我们定义了两个智能体:
main_agent和support_agent。main_agent被设计为初始联系点。 - 当
main_agent调用check_and_transfer工具时,它会检查用户的查询。 - 如果查询包含"urgent"一词,工具会访问
tool_context,特别是tool_context.actions,并将 transfer_to_agent 属性设置为support_agent。 - 此操作向框架发出信号,将对话控制权转移给名为
support_agent的智能体。 - 当
main_agent处理紧急查询时,check_and_transfer工具会触发转移。后续响应理想情况下将来自support_agent。 - 对于没有紧急情况的正常查询,该工具会简单地处理它而不触发转移。
此示例说明了工具如何通过其 ToolContext 中的 EventActions 动态影响对话流程,通过将控制权转移给另一个专业智能体。
身份验证¶
ToolContext 为与已认证 API 交互的工具提供机制。如果您的工具需要处理身份验证,您可以使用以下方法:
-
auth_response(在 Python 中):如果在调用您的工具之前框架已处理身份验证,则包含凭据(例如,令牌)(通常与 RestApiTool 和 OpenAPI 安全方案一起使用)。在 TypeScript 中,通过 getAuthResponse() 方法检索。 -
request_credential(auth_config: dict)(在 Python 中)或requestCredential(authConfig: AuthConfig)(在 TypeScript 中):如果您的工具确定需要身份验证但凭据不可用,请调用此方法。这会通知框架根据提供的 auth_config 启动身份验证流程。 -
get_auth_response()(在 Python 中)或getAuthResponse(authConfig: AuthConfig)(在 TypeScript 中):在后续调用中调用此方法(在 request_credential 成功处理后)以检索用户提供的凭据。
有关身份验证流程、配置和示例的详细说明,请参阅专门的工具身份验证文档页面。
上下文感知数据访问方法¶
这些方法为你的工具提供与会话或用户关联的持久数据交互的便捷方式,这些数据由配置的服务管理。
-
list_artifacts()(在 Python 中)或listArtifacts()(在 Java 和 TypeScript 中):返回通过 artifact_service 为当前会话存储的所有制品的文件名(或键)列表。制品通常是用户上传或由工具/智能体生成的文件(图像、文档等)。 -
load_artifact(filename: str): 从 artifact_service 按其文件名检索特定制品。你可以选择性地指定版本;如果省略,则返回最新版本。返回包含制品数据和 MIME 类型的google.genai.types.Part对象,如果未找到则返回 None。 -
save_artifact(filename: str, artifact: types.Part): 将制品的新版本保存到 artifact_service。返回新版本号(从 0 开始)。 -
search_memory(query: str): (在 ADK Python、Go 和 TypeScript 中支持) 使用配置的memory_service查询用户的长期记忆。这对于从过去的交互或存储的知识中检索相关信息很有用。SearchMemoryResponse 的结构取决于特定的记忆服务实现,但通常包含相关的文本片段或对话摘录。
示例¶
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from google.adk.tools import ToolContext, FunctionTool
from google.genai import types
def process_document(
document_name: str, analysis_query: str, tool_context: ToolContext
) -> dict:
"""Analyzes a document using context from memory."""
# 1. Load the artifact
print(f"Tool: Attempting to load artifact: {document_name}")
document_part = tool_context.load_artifact(document_name)
if not document_part:
return {"status": "error", "message": f"Document '{document_name}' not found."}
document_text = document_part.text # Assuming it's text for simplicity
print(f"Tool: Loaded document '{document_name}' ({len(document_text)} chars).")
# 2. Search memory for related context
print(f"Tool: Searching memory for context related to: '{analysis_query}'")
memory_response = tool_context.search_memory(
f"Context for analyzing document about {analysis_query}"
)
memory_context = "\n".join(
[
m.events[0].content.parts[0].text
for m in memory_response.memories
if m.events and m.events[0].content
]
) # Simplified extraction
print(f"Tool: Found memory context: {memory_context[:100]}...")
# 3. Perform analysis (placeholder)
analysis_result = f"Analysis of '{document_name}' regarding '{analysis_query}' using memory context: [Placeholder Analysis Result]"
print("Tool: Performed analysis.")
# 4. Save the analysis result as a new artifact
analysis_part = types.Part.from_text(text=analysis_result)
new_artifact_name = f"analysis_{document_name}"
version = await tool_context.save_artifact(new_artifact_name, analysis_part)
print(f"Tool: Saved analysis result as '{new_artifact_name}' version {version}.")
return {
"status": "success",
"analysis_artifact": new_artifact_name,
"version": version,
}
doc_analysis_tool = FunctionTool(func=process_document)
# In an Agent:
# Assume artifact 'report.txt' was previously saved.
# Assume memory service is configured and has relevant past data.
# my_agent = Agent(..., tools=[doc_analysis_tool], artifact_service=..., memory_service=...)
import { Part } from "@google/genai";
import { ToolContext } from "@google/adk";
// Analyzes a document using context from memory.
export async function processDocument(
params: { documentName: string; analysisQuery: string },
toolContext?: ToolContext
): Promise<Record<string, any>> {
if (!toolContext) {
throw new Error("ToolContext is required for this tool.");
}
// 1. List all available artifacts
const artifacts = await toolContext.listArtifacts();
console.log(`Listing all available artifacts: ${artifacts}`);
// 2. Load an artifact
console.log(`Tool: Attempting to load artifact: ${params.documentName}`);
const documentPart = await toolContext.loadArtifact(params.documentName);
if (!documentPart) {
console.log(`Tool: Document '${params.documentName}' not found.`);
return {
status: "error",
message: `Document '${params.documentName}' not found.`,
};
}
const documentText = documentPart.text ?? "";
console.log(
`Tool: Loaded document '${params.documentName}' (${documentText.length} chars).`
);
// 3. Search memory for related context
console.log(`Tool: Searching memory for context related to '${params.analysisQuery}'`);
const memory_results = await toolContext.searchMemory(params.analysisQuery);
console.log(`Tool: Found ${memory_results.memories.length} relevant memories.`);
const context_from_memory = memory_results.memories
.map((m) => m.content.parts[0].text)
.join("\n");
// 4. Perform analysis (placeholder)
const analysisResult =
`Analysis of '${params.documentName}' regarding '${params.analysisQuery}':\n` +
`Context from Memory:\n${context_from_memory}\n` +
`[Placeholder Analysis Result]`;
console.log("Tool: Performed analysis.");
// 5. Save the analysis result as a new artifact
const analysisPart: Part = { text: analysisResult };
const newArtifactName = `analysis_${params.documentName}`;
await toolContext.saveArtifact(newArtifactName, analysisPart);
console.log(`Tool: Saved analysis result to '${newArtifactName}'.`);
return {
status: "success",
analysis_artifact: newArtifactName,
};
}
// Copyright 2025 Google LLC
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
type processDocumentArgs struct {
DocumentName string `json:"document_name" jsonschema:"The name of the document to be processed."`
AnalysisQuery string `json:"analysis_query" jsonschema:"The query for the analysis."`
}
type processDocumentResult struct {
Status string `json:"status"`
AnalysisArtifact string `json:"analysis_artifact,omitempty"`
Version int64 `json:"version,omitempty"`
Message string `json:"message,omitempty"`
}
func processDocument(ctx tool.Context, args processDocumentArgs) (*processDocumentResult, error) {
fmt.Printf("Tool: Attempting to load artifact: %s\n", args.DocumentName)
// List all artifacts
listResponse, err := ctx.Artifacts().List(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to list artifacts")
}
fmt.Println("Tool: Available artifacts:")
for _, file := range listResponse.FileNames {
fmt.Printf(" - %s\n", file)
}
documentPart, err := ctx.Artifacts().Load(ctx, args.DocumentName)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("document '%s' not found", args.DocumentName)
}
fmt.Printf("Tool: Loaded document '%s' of size %d bytes.\n", args.DocumentName, len(documentPart.Part.InlineData.Data))
// 3. Search memory for related context
fmt.Printf("Tool: Searching memory for context related to: '%s'\n", args.AnalysisQuery)
memoryResp, err := ctx.SearchMemory(ctx, args.AnalysisQuery)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Tool: Error searching memory: %v\n", err)
}
memoryResultCount := 0
if memoryResp != nil {
memoryResultCount = len(memoryResp.Memories)
}
fmt.Printf("Tool: Found %d memory results.\n", memoryResultCount)
analysisResult := fmt.Sprintf("Analysis of '%s' regarding '%s' using memory context: [Placeholder Analysis Result]", args.DocumentName, args.AnalysisQuery)
fmt.Println("Tool: Performed analysis.")
analysisPart := genai.NewPartFromText(analysisResult)
newArtifactName := fmt.Sprintf("analysis_%s", args.DocumentName)
version, err := ctx.Artifacts().Save(ctx, newArtifactName, analysisPart)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to save artifact")
}
fmt.Printf("Tool: Saved analysis result as '%s' version %d.\n", newArtifactName, version.Version)
return &processDocumentResult{
Status: "success",
AnalysisArtifact: newArtifactName,
Version: version.Version,
}, nil
}
// 使用内存中的上下文分析文档。
// 你还可以使用回调上下文或 LoadArtifacts 工具列出、加载和保存制品。
public static @NonNull Maybe<ImmutableMap<String, Object>> processDocument(
@Annotations.Schema(description = "要分析的文档名称。") String documentName,
@Annotations.Schema(description = "分析的查询。") String analysisQuery,
ToolContext toolContext) {
// 1. 列出所有可用的制品
System.out.printf(
"列出所有可用的制品 %s:", toolContext.listArtifacts().blockingGet());
// 2. 将制品加载到内存
System.out.println("工具:尝试加载制品:" + documentName);
Part documentPart = toolContext.loadArtifact(documentName, Optional.empty()).blockingGet();
if (documentPart == null) {
System.out.println("工具:未找到文档 '" + documentName + "'。");
return Maybe.just(
ImmutableMap.<String, Object>of(
"status", "error", "message", "未找到文档 '" + documentName + "'。"));
}
String documentText = documentPart.text().orElse("");
System.out.println(
"工具:已加载文档 '" + documentName + "' (" + documentText.length() + " 个字符)。");
// 3. 执行分析(占位符)
String analysisResult =
"对 '"
+ documentName
+ "' 关于 '"
+ analysisQuery
+ " [占位符分析结果]";
System.out.println("工具:已执行分析。");
// 4. 将分析结果保存为新制品
Part analysisPart = Part.fromText(analysisResult);
String newArtifactName = "analysis_" + documentName;
toolContext.saveArtifact(newArtifactName, analysisPart);
return Maybe.just(
ImmutableMap.<String, Object>builder()
.put("status", "success")
.put("analysis_artifact", newArtifactName)
.build());
}
// FunctionTool processDocumentTool =
// FunctionTool.create(ToolContextArtifactExample.class, "processDocument");
// 在智能体中,包含此函数工具。
// LlmAgent agent = LlmAgent().builder().tools(processDocumentTool).build();
By leveraging the ToolContext, developers can create more sophisticated and context-aware custom tools that seamlessly integrate with ADK's architecture and enhance the overall capabilities of their agents.
定义有效工具函数¶
将方法或函数用作 ADK 工具时,你如何定义它会显著影响智能体正确使用它的能力。智能体的大语言模型(LLM)严重依赖函数的 名称、参数(参数)、类型提示 和 文档字符串 / 源代码注释 来理解其目的并生成正确的调用。
以下是定义有效工具函数的关键指导原则:
-
函数名称:
- 使用描述性、基于动词 - 名词的名称,清楚地指示操作(例如,
get_weather、searchDocuments、schedule_meeting)。 - 避免通用名称,如
run、process、handle_data,或过于模糊的名称,如doStuff。即使有好的描述,像do_stuff这样的名称也可能在何时使用工具方面使模型混淆,例如与cancelFlight相比。 - LLM 在工具选择期间使用函数名称作为主要标识符。
- 使用描述性、基于动词 - 名词的名称,清楚地指示操作(例如,
-
参数(参数):
- 你的函数可以有任何数量的参数。
- 使用清晰和描述性的名称(例如,
city而不是c,search_query而不是q)。 - 在 Python 中提供类型提示 用于所有参数(例如,
city: str、user_id: int、items: list[str])。这对于 ADK 为 LLM 生成正确模式是必不可少的。 - 确保所有参数类型都是 JSON 可序列化。所有 Java 原始类型以及标准 Python 类型,如
str、int、float、bool、list、dict及其组合通常都是安全的。避免将复杂自定义类实例作为直接参数,除非它们具有清晰的 JSON 表示。 - 不要为参数设置默认值。例如,
def my_func(param1: str = "default")。在函数调用生成期间,底层模型不可靠地支持或使用默认值。所有必要信息都应由 LLM 从上下文派生或在缺失时明确请求。 self/cls自动处理: 像self(对于实例方法)或cls(对于类方法)这样的隐式参数由 ADK 自动处理并从显示给 LLM 的模式中排除。你只需要为工具要求 LLM 提供的逻辑参数定义类型提示和描述。
-
Return Type:
- The function's return value must be a dictionary (
dict) in Python, a Map in Java, or a plain object in TypeScript. - If your function returns a non-dictionary type (e.g., a string, number, list), the ADK framework will automatically wrap it into a dictionary/Map like
{'result': your_original_return_value}before passing the result back to the model. - Design the dictionary/Map keys and values to be descriptive and easily understood by the LLM. Remember, the model reads this output to decide its next step.
- Include meaningful keys. For example, instead of returning just an error code like
500, return{'status': 'error', 'error_message': 'Database connection failed'}. - It's a highly recommended practice to include a
statuskey (e.g.,'success','error','pending','ambiguous') to clearly indicate the outcome of the tool execution for the model.
- The function's return value must be a dictionary (
-
文档字符串 / 源代码注释:
- 这很关键。 文档字符串是 LLM 的描述性信息的主要来源。
- 清楚地说明工具做什么。 具体说明其目的和局限性。
- 解释何时应使用工具。 提供上下文或示例场景以指导 LLM 的决策。
- 清楚地描述每个参数。 解释 LLM 需要为该参数提供什么信息。
- 描述 预期
dict返回值的结构和含义,特别是不同的status值和相关的数据键。 - 不要描述注入的 ToolContext 参数。避免在文档字符串描述中提及可选的
tool_context: ToolContext参数,因为这不是 LLM 需要知道的参数。ToolContext 是由 ADK 注入的,在 LLM 决定调用它之后。
良好定义的示例:
def lookup_order_status(order_id: str) -> dict:
"""使用其 ID 获取客户订单的当前状态。
仅当用户明确询问特定订单的状态并提供订单 ID 时才使用此工具。不要将其用于
一般查询。
Args:
order_id: 要查找的订单的唯一标识符。
Returns:
指示结果的字典。
成功时,状态为 'success' 并包含 'order' 字典。
失败时,状态为 'error' 并包含 'error_message'。
成功示例:{'status': 'success', 'order': {'state': 'shipped', 'tracking_number': '1Z9...'}}
错误示例:{'status': 'error', 'error_message': f"Order ID {order_id} not found."}
"""
# ... 获取状态的函数实现 ...
if status_details := fetch_status_from_backend(order_id):
return {
"status": "success",
"order": {
"state": status_details.state,
"tracking_number": status_details.tracking,
},
}
else:
return {"status": "error", "error_message": f"Order ID {order_id} not found."}
/**
* Fetches the current status of a customer's order using its ID.
*
* Use this tool ONLY when a user explicitly asks for the status of
* a specific order and provides the order ID. Do not use it for
* general inquiries.
*
* @param params The parameters for the function.
* @param params.order_id The unique identifier of the order to look up.
* @returns A dictionary indicating the outcome.
* On success, status is 'success' and includes an 'order' dictionary.
* On failure, status is 'error' and includes an 'error_message'.
* Example success: {'status': 'success', 'order': {'state': 'shipped', 'tracking_number': '1Z9...'}}
* Example error: {'status': 'error', 'error_message': 'Order ID not found.'}
*/
async function lookupOrderStatus(params: { order_id: string }): Promise<Record<string, any>> {
// ... function implementation to fetch status from a backend ...
const status_details = await fetchStatusFromBackend(params.order_id);
if (status_details) {
return {
"status": "success",
"order": {
"state": status_details.state,
"tracking_number": status_details.tracking,
},
};
} else {
return { "status": "error", "error_message": `Order ID ${params.order_id} not found.` };
}
}
// Placeholder for a backend call
async function fetchStatusFromBackend(order_id: string): Promise<{state: string, tracking: string} | null> {
if (order_id === "12345") {
return { state: "shipped", tracking: "1Z9..." };
}
return null;
}
import (
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/adk/tool"
)
type lookupOrderStatusArgs struct {
OrderID string `json:"order_id" jsonschema:"The ID of the order to look up."`
}
type order struct {
State string `json:"state"`
TrackingNumber string `json:"tracking_number"`
}
type lookupOrderStatusResult struct {
Status string `json:"status"`
Order order `json:"order,omitempty"`
}
func lookupOrderStatus(ctx tool.Context, args lookupOrderStatusArgs) (*lookupOrderStatusResult, error) {
// ... function implementation to fetch status ...
statusDetails, ok := fetchStatusFromBackend(args.OrderID)
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("order ID %s not found", args.OrderID)
}
return &lookupOrderStatusResult{
Status: "success",
Order: order{
State: statusDetails.State,
TrackingNumber: statusDetails.Tracking,
},
}, nil
}
/**
* 检索指定城市的当前天气报告。
*
* @param city 要检索天气报告的城市。
* @param toolContext 工具的上下文。
* @return 包含天气信息的字典。
*/
public static Map<String, Object> getWeatherReport(String city, ToolContext toolContext) {
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
if (city.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).equals("london")) {
response.put("status", "success");
response.put(
"report",
"The current weather in London is cloudy with a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius and a"
+ " chance of rain.");
} else if (city.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).equals("paris")) {
response.put("status", "success");
response.put("report", "The weather in Paris is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius.");
} else {
response.put("status", "error");
response.put("error_message", String.format("Weather information for '%s' is not available.", city));
}
return response;
}
- Simplicity and Focus:
- Keep Tools Focused: Each tool should ideally perform one well-defined task.
- Fewer Parameters are Better: Models generally handle tools with fewer, clearly defined parameters more reliably than those with many optional or complex ones.
- Use Simple Data Types: Prefer basic types (
str,int,bool,float,List[str], in Python;int,byte,short,long,float,double,booleanandcharin Java; orstring,number,boolean, and arrays likestring[]in TypeScript) over complex custom classes or deeply nested structures as parameters when possible. - Decompose Complex Tasks: Break down functions that perform multiple distinct logical steps into smaller, more focused tools. For instance, instead of a single
update_user_profile(profile: ProfileObject)tool, consider separate tools likeupdate_user_name(name: str),update_user_address(address: str),update_user_preferences(preferences: list[str]), etc. This makes it easier for the LLM to select and use the correct capability.
通过遵循这些指导原则,你为 LLM 提供了有效利用你的自定义函数工具所需的清晰度和结构,从而实现更强大和可靠的智能体行为。
工具集:分组和动态提供工具¶
Beyond individual tools, ADK introduces the concept of a Toolset via the BaseToolset interface (defined in google.adk.tools.base_toolset). A toolset allows you to manage and provide a collection of BaseTool instances, often dynamically, to an agent.
这种方法的好处包括:
- 组织相关工具: 将服务于共同目的的工具分组(例如,所有用于数学运算的工具,或所有与特定 API 交互的工具)。
- 动态工具可用性: 使智能体能够根据当前上下文(例如,用户权限、会话状态或其他运行时条件)使用不同的可用工具。工具集的
get_tools方法可以决定暴露哪些工具。 - 集成外部工具提供者: 工具集可以作为来自外部系统(如 OpenAPI 规范或 MCP 服务器)的工具的适配器,将它们转换为 ADK 兼容的
BaseTool对象。
BaseToolset 接口¶
任何在 ADK 中作为工具集的类都应实现 BaseToolset 抽象基类。此接口主要定义了两种方法:
-
async def get_tools(...) -> list[BaseTool]:这是工具集的核心方法。当 ADK 智能体需要知道其可用工具时,它将在其tools列表中提供的每个BaseToolset实例上调用get_tools()。- 它接收一个可选的
readonly_context(ReadonlyContext的实例)。此上下文提供对信息的只读访问,如当前会话状态(readonly_context.state)、智能体名称和调用 ID。工具集可以使用此上下文动态决定返回哪些工具。 - 它必须返回
BaseTool实例的list(例如,FunctionTool、RestApiTool)。
- 它接收一个可选的
-
async def close(self) -> None:当工具集不再需要时,例如当智能体服务器关闭或Runner正在关闭时,ADK 框架会调用此异步方法。实现此方法以执行任何必要的清理,例如关闭网络连接、释放文件句柄或清理工具集管理的其他资源。
将工具集与智能体一起使用¶
你可以将 BaseToolset 实现的实例直接包含在 LlmAgent 的 tools 列表中,与单个 BaseTool 实例一起。
当智能体初始化或需要确定其可用功能时,ADK 框架将遍历 tools 列表:
- 如果项目是
BaseTool实例,则直接使用它。 - 如果项目是
BaseToolset实例,则调用其get_tools()方法(使用当前ReadonlyContext),并将返回的BaseTool列表添加到智能体的可用工具中。
示例:简单数学工具集¶
让我们创建一个提供简单算术运算的工具集的基本示例。
# 1. Define the individual tool functions
def add_numbers(a: int, b: int, tool_context: ToolContext) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Adds two integer numbers.
Args:
a: The first number.
b: The second number.
Returns:
A dictionary with the sum, e.g., {'status': 'success', 'result': 5}
"""
print(f"Tool: add_numbers called with a={a}, b={b}")
result = a + b
# Example: Storing something in tool_context state
tool_context.state["last_math_operation"] = "addition"
return {"status": "success", "result": result}
def subtract_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Subtracts the second number from the first.
Args:
a: The first number.
b: The second number.
Returns:
A dictionary with the difference, e.g., {'status': 'success', 'result': 1}
"""
print(f"Tool: subtract_numbers called with a={a}, b={b}")
return {"status": "success", "result": a - b}
# 2. Create the Toolset by implementing BaseToolset
class SimpleMathToolset(BaseToolset):
def __init__(self, prefix: str = "math_"):
self.prefix = prefix
# Create FunctionTool instances once
self._add_tool = FunctionTool(
func=add_numbers,
name=f"{self.prefix}add_numbers", # Toolset can customize names
)
self._subtract_tool = FunctionTool(
func=subtract_numbers, name=f"{self.prefix}subtract_numbers"
)
print(f"SimpleMathToolset initialized with prefix '{self.prefix}'")
async def get_tools(
self, readonly_context: Optional[ReadonlyContext] = None
) -> List[BaseTool]:
print(f"SimpleMathToolset.get_tools() called.")
# Example of dynamic behavior:
# Could use readonly_context.state to decide which tools to return
# For instance, if readonly_context.state.get("enable_advanced_math"):
# return [self._add_tool, self._subtract_tool, self._multiply_tool]
# For this simple example, always return both tools
tools_to_return = [self._add_tool, self._subtract_tool]
print(f"SimpleMathToolset providing tools: {[t.name for t in tools_to_return]}")
return tools_to_return
async def close(self) -> None:
# No resources to clean up in this simple example
print(f"SimpleMathToolset.close() called for prefix '{self.prefix}'.")
await asyncio.sleep(0) # Placeholder for async cleanup if needed
# 3. Define an individual tool (not part of the toolset)
def greet_user(name: str = "User") -> Dict[str, str]:
"""Greets the user."""
print(f"Tool: greet_user called with name={name}")
return {"greeting": f"Hello, {name}!"}
greet_tool = FunctionTool(func=greet_user)
# 4. Instantiate the toolset
math_toolset_instance = SimpleMathToolset(prefix="calculator_")
# 5. Define an agent that uses both the individual tool and the toolset
calculator_agent = LlmAgent(
name="CalculatorAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Replace with your desired model
instruction="You are a helpful calculator and greeter. "
"Use 'greet_user' for greetings. "
"Use 'calculator_add_numbers' to add and 'calculator_subtract_numbers' to subtract. "
"Announce the state of 'last_math_operation' if it's set.",
tools=[greet_tool, math_toolset_instance], # Individual tool # Toolset instance
)
/**
* Copyright 2025 Google LLC
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import { LlmAgent, FunctionTool, ToolContext, BaseToolset, InMemoryRunner, isFinalResponse, BaseTool, stringifyContent } from "@google/adk";
import { z } from "zod";
import { Content, createUserContent } from "@google/genai";
function addNumbers(params: { a: number; b: number }, toolContext?: ToolContext): Record<string, any> {
if (!toolContext) {
throw new Error("ToolContext is required for this tool.");
}
const result = params.a + params.b;
toolContext.state.set("last_math_result", result);
return { result: result };
}
function subtractNumbers(params: { a: number; b: number }): Record<string, any> {
return { result: params.a - params.b };
}
function greetUser(params: { name: string }): Record<string, any> {
return { greeting: `Hello, ${params.name}!` };
}
class SimpleMathToolset extends BaseToolset {
private readonly tools: BaseTool[];
constructor(prefix = "") {
super([]); // No filter
this.tools = [
new FunctionTool({
name: `${prefix}add_numbers`,
description: "Adds two numbers and stores the result in the session state.",
parameters: z.object({ a: z.number(), b: z.number() }),
execute: addNumbers,
}),
new FunctionTool({
name: `${prefix}subtract_numbers`,
description: "Subtracts the second number from the first.",
parameters: z.object({ a: z.number(), b: z.number() }),
execute: subtractNumbers,
}),
];
}
async getTools(): Promise<BaseTool[]> {
return this.tools;
}
async close(): Promise<void> {
console.log("SimpleMathToolset closed.");
}
}
async function main() {
const mathToolset = new SimpleMathToolset("calculator_");
const greetTool = new FunctionTool({
name: "greet_user",
description: "Greets the user.",
parameters: z.object({ name: z.string() }),
execute: greetUser,
});
const instruction =
`You are a calculator and a greeter.
If the user asks for a math operation, use the calculator tools.
If the user asks for a greeting, use the greet_user tool.
The result of the last math operation is stored in the 'last_math_result' state variable.`;
const calculatorAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: "calculator_agent",
instruction: instruction,
tools: [greetTool, mathToolset],
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
});
const runner = new InMemoryRunner({ agent: calculatorAgent, appName: "toolset_app" });
await runner.sessionService.createSession({ appName: "toolset_app", userId: "user1", sessionId: "session1" });
const message: Content = createUserContent("What is 5 + 3?");
for await (const event of runner.runAsync({ userId: "user1", sessionId: "session1", newMessage: message })) {
if (isFinalResponse(event) && event.content?.parts?.length) {
const text = stringifyContent(event).trim();
if (text) {
console.log(`Response from agent: ${text}`);
}
}
}
await mathToolset.close();
}
main();
在此示例中:
SimpleMathToolset实现BaseToolset,其get_tools()方法返回add_numbers和subtract_numbers的FunctionTool实例。它还使用前缀自定义它们的名称。calculator_agent配置了单个greet_tool和SimpleMathToolset的实例。- 当运行
calculator_agent时,ADK 将调用math_toolset_instance.get_tools()。智能体的 LLM 将能够访问greet_user、calculator_add_numbers和calculator_subtract_numbers以处理用户请求。 add_numbers工具演示写入tool_context.state,智能体的指令提到读取此状态。- 调用
close()方法以确保工具集持有的任何资源都得到释放。
工具集为组织、管理和动态提供工具集合到你的 ADK 智能体提供了强大的方式,从而实现更模块化、可维护和可适应的智能体应用程序。